Table of Contents
Modern flow meters play a crucial role in industries like agriculture, manufacturing, and water management. By linking these devices to a computer, users gain real-time insights into liquid movement, improving efficiency and accuracy.
Digital integration allows for instant tracking of usage patterns. Whether monitoring irrigation systems or industrial processes, automated data collection reduces manual errors. This ensures reliable measurements for critical applications.
Options range from wired connections like USB to wireless IoT solutions. Each method offers unique advantages depending on the environment. Proper setup guarantees precise readings for water and other fluids.
This guide covers essential steps for seamless device pairing. From hardware selection to software configuration, you’ll learn best practices for optimal performance.
Why Connect a Flow Meter to a Computer?
Integrating measurement devices with digital systems transforms how industries track liquid movement. Real-time insights improve decision-making and operational efficiency. This setup eliminates guesswork by delivering precise data instantly.
Instant Access to Critical Metrics
Continuous monitoring provides live updates on flow rates and consumption patterns. Operators can spot irregularities immediately, preventing costly downtime. For example, sudden drops may indicate leaks or blockages needing urgent attention.
Modern software solutions display metrics through intuitive dashboards. Visual graphs and color-coded alerts simplify complex data interpretation. This helps teams respond faster to changing conditions.
Advanced Data Management Capabilities
Digital systems automatically log measurements with timestamps for historical analysis. Stored records help identify trends over weeks or months. Teams can generate reports showing peak usage periods or equipment performance.
| Feature | Manual Recording | Computerized System |
|---|---|---|
| Data Accuracy | Prone to human error | 99.9% precision |
| Storage Capacity | Limited notebooks | Unlimited cloud backups |
| Analysis Speed | Hours per report | Real-time processing |
Remote Supervision and Notifications
Cellular-enabled devices like Reporter send SMS alerts for pump failures or overflow risks. Field personnel receive warnings directly on their phones, enabling swift action. Secure VPN connections allow engineers to access industrial networks from any location.
Aquafin’s smart solution reduced overflow incidents by 68% through automated alerts. Their system triggers warnings when liquid levels approach critical thresholds. This case demonstrates how digital integration enhances control over fluid management.
For comprehensive guidance on setting up these features, explore our detailed flow meter integration tutorial.
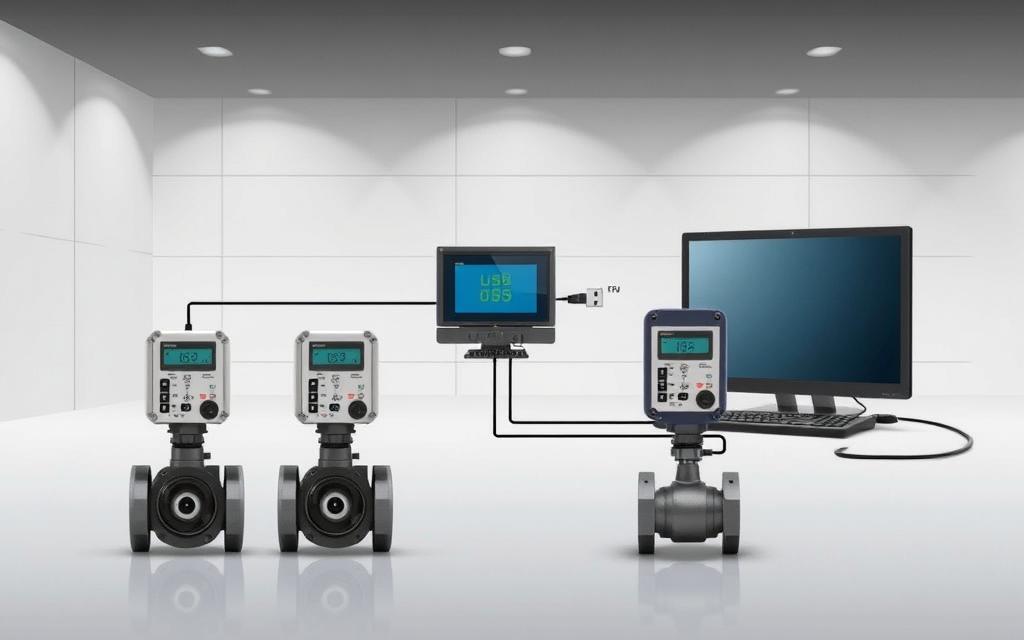
Essential Tools for Connecting a Flow Meter
Accurate fluid measurement requires the right hardware and software components. Compatibility ensures seamless data transfer between devices and systems. Below are the critical elements for a functional setup.

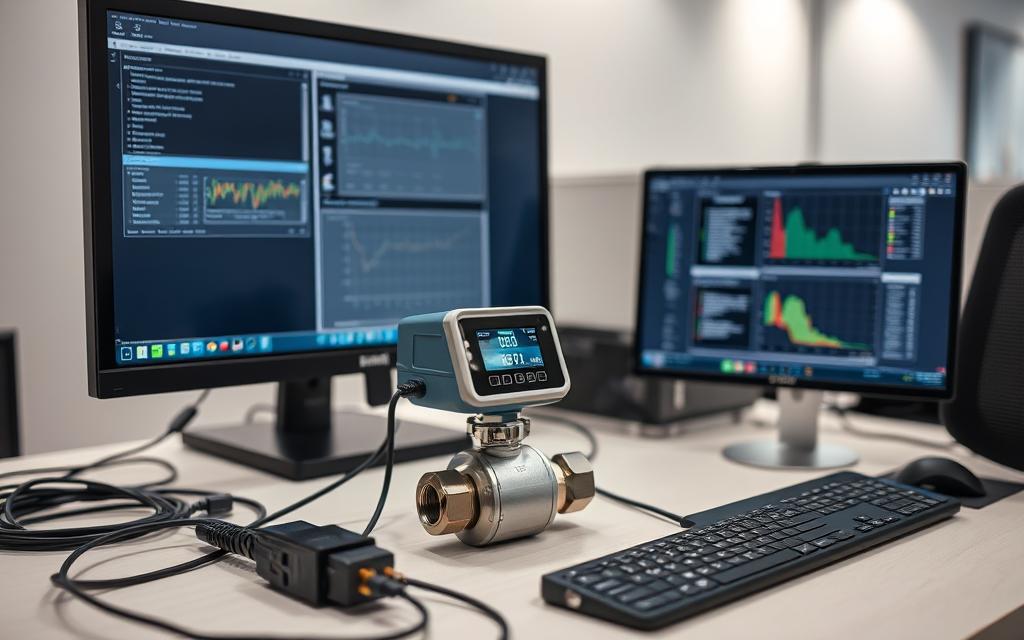
Flow Meter with Communication Ports
Modern meters feature RS-485, USB, or Ethernet ports for digital output. Verify your device supports industry-standard protocols like Modbus. Legacy models may need pulse-to-analog converters for integration.
Computer and Cables
A stable PC with updated drivers is essential. Use shielded cables to reduce interference in industrial environments. Reporter’s sensor adapters simplify connections for diverse meter types.
Software and Adapters
Install the manufacturer’s software or third-party programs like Crodeon Dashboard. Open-source options like Arduino IDE suit DIY projects. Always check version compatibility with your OS.
Adjust communication settings to match baud rates and parity bits. This solution prevents data mismatches during transmission. Proper tools ensure reliable, real-time monitoring.
Step-by-Step: How to Connect Flow Meter to Computer
Efficient fluid monitoring starts with compatible communication ports. Proper setup ensures seamless data transfer between your device and digital systems. Follow these steps for error-free integration.
Step 1: Identify the Communication Port
Locate the output interface on your device—common options include:
- RS-232/RS-485 for industrial environments
- USB for plug-and-play setups
- Ethernet for networked systems
Check the manufacturer’s manual for port specifications. Older models may require adapters for digital output.
Step 2: Select the Connection Method
Choose a method based on your hardware and environment:
- USB: Ideal for short-range setups; use shielded cables to reduce interference.
- RS232: Requires serial-to-USB adapters; configure baud rates in device settings.
- Ethernet: Enables remote access via LAN/WAN networks.
Step 3: Install Required Software
Use the manufacturer’s software or third-party programs like Crodeon Dashboard. Key actions include:
- Downloading the latest driver version (e.g., Endress+Hauser Fieldcare).
- Creating virtual COM ports for USB-serial adapters.
- Running the calibration wizard in LabVIEW DAQ systems for precise readings.
Ensure the application matches your operating system to avoid compatibility issues.
Configuring USB and Serial Connections
Establishing reliable communication between measurement devices and digital systems requires proper configuration. Each connection type—USB, serial, or Ethernet—demands specific settings for optimal performance. Below are detailed steps for seamless integration.

USB Connection Setup
For plug-and-play simplicity, USB is ideal for short-range setups. Ensure the device drivers are installed before connecting. Shielded cables minimize interference in electrically noisy environments.
Most modern meters auto-detect via USB. If not, manually assign a virtual COM port in the application settings. Verify baud rates match the device specifications.
RS232/RS485 Connection Setup
Industrial environments often use RS232 or RS485 for robustness. These serial protocols require converters for modern PCs. Configure parity bits and stop bits in the software to align with the meter’s output.
Reporter’s adapters simplify RS485-to-USB conversion. Test the connection with terminal software like PuTTY before full integration.
Ethernet and Network Configuration
Ethernet/IP setups enable remote monitoring and scalable deployments. VLAN segmentation enhances industrial network security by isolating sensor traffic. Port forwarding allows external Modbus TCP access.
For Reporter devices, assign static IPs to ensure stable communication. Integrate SNMP monitoring to track network health and detect disruptions proactively.
“Proper VLAN design prevents unauthorized access to critical measurement data.”
This solution ensures real-time data flows securely across distributed systems. Always test configurations under operational conditions to confirm reliability.
Setting Up Flow Meter Software
Proper software configuration transforms raw measurements into actionable insights. The right tools ensure precise flow rate tracking and seamless integration with analytics platforms. Below are critical steps to optimize performance.
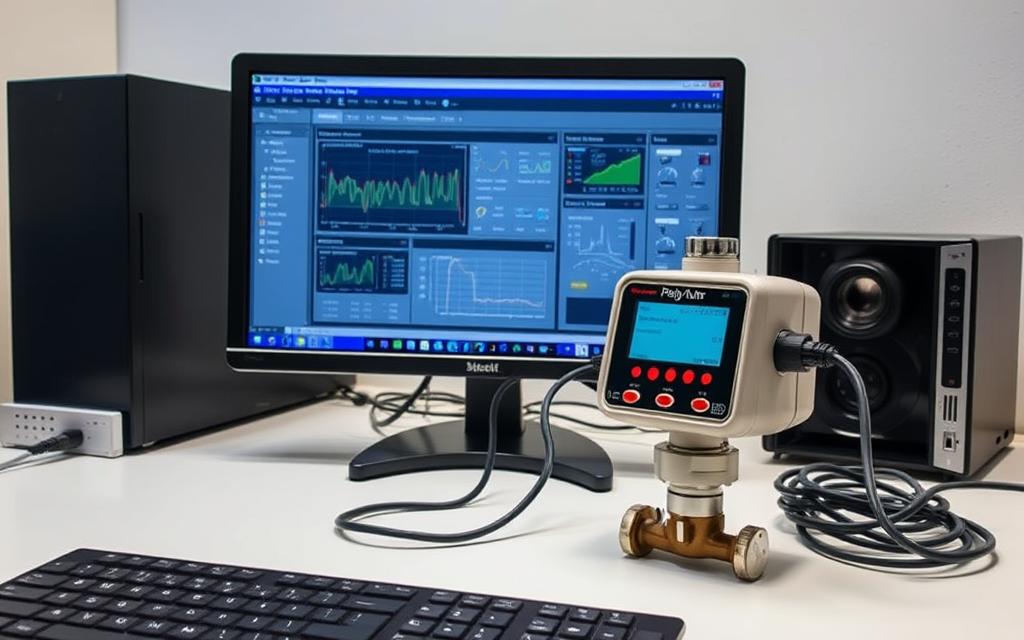

Selecting the Correct Communication Protocol
Match the protocol to your device’s output for accurate data transfer. Common options include:
- Modbus RTU for industrial RS485 networks
- HART for analog-digital hybrid systems
- EtherNet/IP for high-speed factory networks
Verify the meter’s documentation for supported protocols. Mismatched settings cause transmission errors.
Testing the Connection
Validate communication before full deployment. Use terminal software like TeraTerm to check live flow rate signals. Look for consistent values without dropouts.
Reporter’s diagnostic tools flag CRC errors or timeouts. Resolve issues by adjusting baud rates or cable shielding.
Calibrating for Accurate Readings
Calibration aligns sensor output with real-world conditions. Follow these standards:
| Method | Accuracy | Application |
|---|---|---|
| Deadweight Tester | ±0.025% | Pressure-dependent systems |
| Master Meter Prover | ±0.5% | Field verification |
| ISO 4064 | ±1% | Water meter certification |
For best results, calibrate under typical operating conditions. Record baseline measurements to detect drift over time.
Monitoring and Recording Flow Data
Tracking fluid movement digitally unlocks powerful operational insights. Advanced software converts raw measurements into actionable trends. This control capability helps teams optimize processes and reduce waste.
Live Data Visualization
Interactive dashboards display real-time monitoring metrics. Color-coded graphs highlight normal ranges versus anomalies. Operators can spot issues like sudden pressure drops instantly.
Customizable views show:
- Hourly consumption patterns
- Equipment performance benchmarks
- System efficiency ratings
Exporting Data to Excel or CSV
Most software supports one-click exports for analysis. CSV files preserve timestamp accuracy for audits. Excel templates can automate monthly reporting.
For compliance purposes:
- Set automatic daily backups
- Include metadata like calibration dates
- Use standardized column headers
Setting Up Alerts for Anomalies
Configure threshold-based alerts for critical conditions. This solution prevents overflow incidents and equipment damage. Smart systems even suggest corrective actions.
“Deadband settings of ±5% reduce false alarms by 73% in water systems.”
For urgent issues, integrate SMS gateways via API. Escalation protocols ensure the right personnel receive notifications. Continuous monitoring keeps operations running smoothly.
Troubleshooting Common Connection Issues
Diagnosing connection problems early prevents costly operational delays. Even robust systems encounter glitches, but quick fixes restore accurate control over fluid measurements. Below are proven methods to resolve frequent challenges.
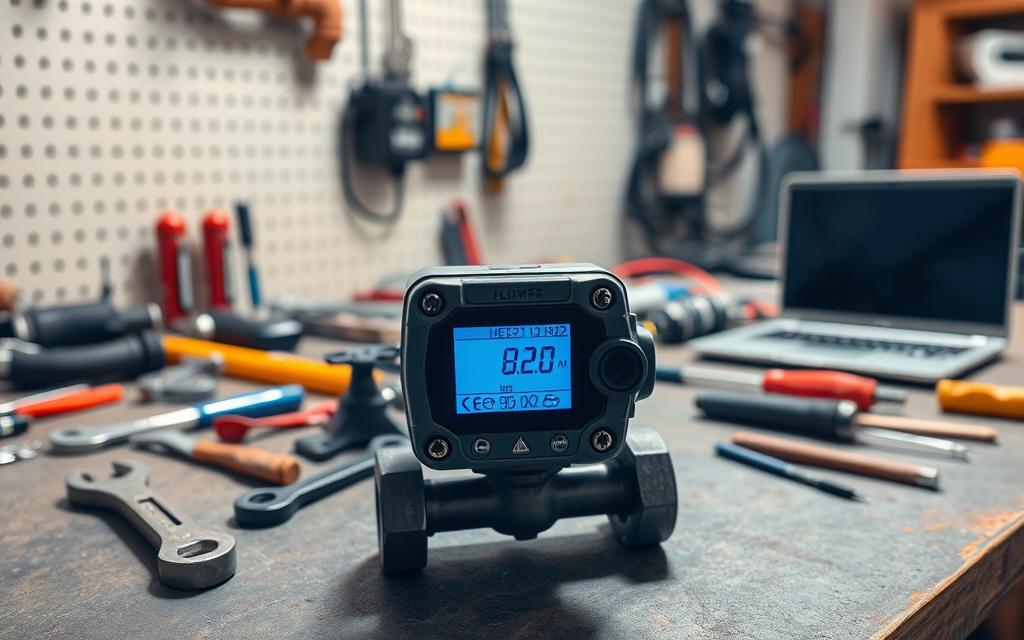

No Communication Detected
Check physical connections first. Loose cables or corroded ports often disrupt signals. Verify power supplies and grounding to eliminate electrical interference.
In software, confirm COM port assignments match device outputs. Restarting the application refreshes communication channels. For networked systems, ping tests identify packet loss.
Incorrect or Missing Data
Mismatched baud rates cause garbled transmissions. Cross-reference device manuals for correct settings. Use terminal emulators like TeraTerm to validate raw data streams.
Calibration drift may skew readings. Recalibrate using master meters or deadweight testers. Log baseline values for future comparisons.
Adapter and Driver Problems
Enterprise systems require WHQL-signed drivers for stability. Key considerations include:
- Version compatibility with OS updates
- Linux kernel modules for custom hardware
- Oscilloscope checks for USB voltage fluctuations
“Driver conflicts account for 42% of industrial sensor communication failures.”
This solution ensures seamless integration across diverse environments. Regular driver updates maintain peak performance.
Conclusion: Streamlining Flow Meter Integration
Digital transformation in fluid measurement systems enhances operational efficiency. Modern flow meters paired with IoT solutions reduce long-term costs through automated data collection. This minimizes manual errors while boosting accuracy.
Future-proof setups leverage software-defined instrumentation. Upgradable firmware ensures compatibility with evolving industrial standards. Secure monitoring protocols like IEC 62443 protect sensitive flow meter networks from breaches.
Reporter devices exemplify this shift. Their cloud-based analytics optimize resource allocation. By integrating these tools, industries gain real-time insights while maintaining compliance. The right solution transforms raw metrics into actionable intelligence.
FAQ
What are the benefits of linking a flow meter to a computer?
Connecting enables real-time monitoring, automated data logging, and remote access for alerts. It improves accuracy and efficiency in industrial or laboratory settings.
Which flow meters support computer connectivity?
Models with USB, RS232/RS485, or Ethernet ports work best. Brands like Siemens, Endress+Hauser, and Badger Meter offer compatible options.
What software is needed to read flow meter data?
Manufacturer-specific programs (e.g., PanaView for Panametrics) or third-party DAQ tools like LabVIEW process pulse outputs and analog signals.
How do I troubleshoot a failed connection?
Verify port settings, update drivers, and check cables. Incorrect baud rate or protocol mismatches often cause issues.
Can I export flow rate data for analysis?
Yes. Most software exports readings to Excel, CSV, or SQL databases for trend analysis and reporting.
Is calibration required after setup?
Yes. Calibrate using a known flow standard to ensure measurements match the software’s displayed values.
What’s the difference between pulse and analog outputs?
Pulse outputs count discrete signals per volume unit, while analog outputs (4-20mA/0-10V) provide continuous rate data.
How do I configure alerts for abnormal flow rates?
Use software like FlowWorks or SCADA systems to set thresholds. Alerts trigger via email or SMS if values exceed limits.