Table of Contents
Bitcoin is a peer-to-peer, cross-border payment system that offers transactions for a fraction of the cost and double the speed of traditional financial institutions.
To initiate a transaction, you’ll need the recipient’s BTC wallet address and the amount you wish to transfer. Understanding the basics of Bitcoin wallets and addresses is crucial for sending and receiving cryptocurrency.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through the process of sending Bitcoin, covering the technical aspects behind transactions, including blockchain verification and processing, as well as transaction fees and security best practices.
By the end of this guide, you’ll be able to confidently send Bitcoin to a friend, make a purchase, or transfer funds between your own wallets on the network.
Understanding Bitcoin Wallets and Addresses
The foundation of sending Bitcoin lies in comprehending the function and importance of Bitcoin wallets. A Bitcoin wallet is essential for managing your cryptocurrency, enabling you to send, receive, and secure your Bitcoin holdings.
What Is a Bitcoin Wallet?
A Bitcoin wallet is not a physical container but a software application or hardware device that stores your private keys, allowing interaction with the Bitcoin blockchain. According to Investopedia, a Bitcoin wallet’s primary function is to generate and store private keys, which control your Bitcoin accounts. There are various types of Bitcoin wallets, including software wallets (mobile, desktop, web-based) and hardware wallets, each offering different levels of security and convenience.
Bitcoin Addresses Explained
Your Bitcoin wallet generates and manages Bitcoin addresses, which serve as your account numbers on the blockchain. These addresses are unique alphanumeric identifiers derived from your wallet’s public key through cryptographic functions. For enhanced privacy and security, most Bitcoin wallets automatically generate a new address for each transaction. Understanding how Bitcoin addresses work is crucial for managing your cryptocurrency effectively.
| Wallet Type | Security Level | Convenience |
|---|---|---|
| Software Wallet | Medium | High |
| Hardware Wallet | High | Medium |
Prerequisites for Sending Bitcoin
Before diving into the process of sending Bitcoin, it’s essential to understand the prerequisites that lay the groundwork for a smooth transaction. Two critical steps are involved: setting up your Bitcoin wallet and acquiring Bitcoin to send.
Setting Up Your Bitcoin Wallet
Setting up a Bitcoin wallet is the first step towards sending Bitcoin. You can choose from various types of wallets, including software wallets that operate on your smartphone or laptop, and hardware wallets that sign transactions offline, keeping your private keys safe from online threats. When choosing a wallet, consider factors such as security features, user interface, and backup options.
The setup process typically involves downloading the wallet application, creating a new wallet, and securely backing up your recovery phrase or seed words. This step is critical as it allows you to restore access to your cryptocurrency if your device is lost or damaged.
Acquiring Bitcoin to Send
After setting up your wallet, you’ll need to acquire Bitcoin through various methods such as purchasing from cryptocurrency exchanges, Bitcoin ATMs, peer-to-peer platforms, or receiving it as payment for goods and services. When purchasing Bitcoin from exchanges, you’ll typically need to complete identity verification procedures and connect a payment method.
| Method | Description | Security Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Cryptocurrency Exchanges | Purchase Bitcoin using traditional currency | Complete identity verification, secure payment methods |
| Bitcoin ATMs | Use cash to buy Bitcoin | Be aware of ATM fees and limits |
| Peer-to-Peer Platforms | Buy Bitcoin directly from other users | Ensure you’re using a reputable platform |

How to Send Bitcoin: The Complete Process
The process of sending Bitcoin requires attention to detail and adherence to a few key steps. To successfully transfer Bitcoin, you must first understand the mechanics involved in the transaction process.
Step 1: Obtain the Recipient’s Bitcoin Address
To initiate a Bitcoin transaction, you need to obtain the recipient’s Bitcoin wallet address. This can be done by receiving the address directly from the recipient or by having them share it via a QR code. It’s crucial to double-check the address to avoid errors, as Bitcoin transactions are irreversible. You can either manually type the address (not recommended due to the risk of typos), copy and paste it, or scan the QR code using your wallet app’s camera function—the latter being the most convenient and least error-prone method.
Step 2: Enter the Amount to Send
After obtaining the recipient’s Bitcoin address, the next step is to specify the amount of Bitcoin you wish to send. Most wallets allow you to enter the amount either in BTC (e.g., 0.001 BTC) or in a fiat currency equivalent (e.g., $50 worth of BTC). Ensure you have enough Bitcoin to cover both the amount you want to send and the transaction fee, which varies based on network congestion.
Step 3: Review and Confirm the Transaction
Before finalizing the transaction, it’s essential to review all the details carefully, including the recipient’s address, the amount you’re sending, and the transaction fee. Once you’ve confirmed that all information is correct, you can proceed to confirm the transaction through your wallet’s confirmation mechanism, which may involve password entry, biometric verification, or a hardware wallet button press. After confirmation, your transaction is broadcast to the Bitcoin network and awaits verification.
To track the progress of your transaction, most wallets provide a transaction ID or hash that you can use on blockchain explorers. The time it takes for the recipient to receive the funds depends on network conditions and the number of confirmations required.
Understanding Bitcoin Transaction Fees
When sending Bitcoin, it’s vital to comprehend the transaction fees involved. Every action on the Bitcoin blockchain incurs a network fee, also known as a gas fee, which is paid to miners for processing transactions.
How Bitcoin Network Fees Work
The Bitcoin network fee is the amount of BTC you pay to process your transaction on the Bitcoin network. The fee goes to miners, who execute your transaction. The cost depends on the size of the transaction and the network usage at the time. The basic formula to calculate fees is: Transaction Fee = Transaction Size × Fee Rate. Network fees serve two purposes: they protect the blockchain from spam and incentivize network participants.
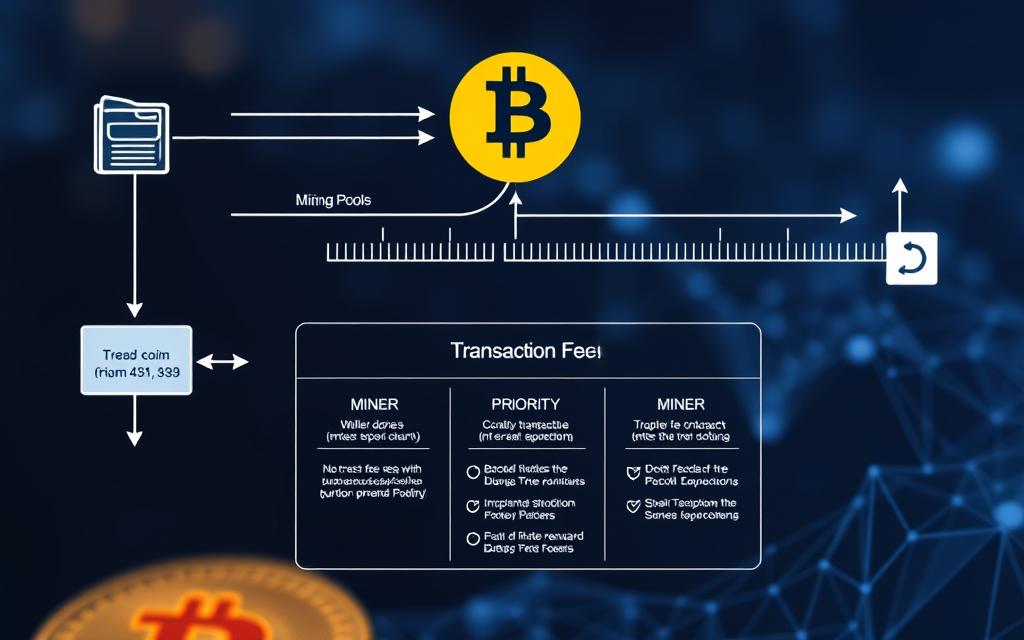
Choosing the Right Fee for Your Transaction
Most Bitcoin wallets automatically suggest appropriate fee levels based on current network conditions, often offering options like “slow” (lower fee, longer wait time), “medium,” or “fast” (higher fee, quicker confirmation). Advanced users can manually set custom fee rates in many wallets, potentially saving money during non-urgent transactions by accepting longer confirmation times. Some wallets also offer fee-bumping features that allow you to increase your transaction fee if your transaction is taking too long to confirm due to changing network conditions.
Security Considerations When Sending Bitcoin
The security of your Bitcoin transactions is paramount. Ensuring that your transactions are secure involves several key considerations.
Double-Checking Recipient Addresses
One of the most critical security measures is to double-check the recipient’s Bitcoin address before confirming a transaction. Bitcoin transactions are irreversible, meaning that if you send Bitcoin to the wrong address, you cannot retrieve it. Malware can even alter the address in your clipboard, replacing it with a hacker’s address. Always verify the entire address character by character.
To further mitigate risks, consider sending a small test transaction before transferring larger amounts, especially when using a new recipient address for the first time.
Using Secure Connections and Hardware Wallets
Using a hardware wallet provides enhanced security for your Bitcoin transactions. Hardware wallets sign transactions offline, keeping your private keys away from internet-connected devices and thus protecting them from online threats. When you need to send Bitcoin, the transaction is signed offline and then sent to the blockchain via your smartphone or laptop.
Additionally, be cautious when using public Wi-Fi networks, as they can be compromised by attackers. Enable all available security features in your Bitcoin wallet, such as PIN codes, passwords, and two-factor authentication, to prevent unauthorized access. Regularly updating your wallet software is also crucial to ensure you have the latest security patches.
Conclusion
Mastering the process of sending Bitcoin is now within your reach. To send bitcoins with confidence, first obtain a Bitcoin wallet, then acquire the recipient’s public address and choose an amount to send. Review the transaction details, including any transaction fees, before hitting ‘Send’. As cryptocurrency adoption grows, more services are integrating Bitcoin payment options, making it increasingly useful for everyday transactions. With practice, sending BTC becomes straightforward, offering a decentralized alternative to traditional banking systems.
FAQ
What is the minimum amount of cryptocurrency I can send?
The minimum amount of cryptocurrency you can send varies depending on the blockchain network and the wallet you’re using. Some wallets and exchanges have minimum transaction limits, while others may allow you to send any amount, including very small fractions of a BTC.
How long does a cryptocurrency transaction take to process?
The processing time for a cryptocurrency transaction depends on several factors, including the network congestion, the transaction fee paid, and the specific cryptocurrency being sent. On average, a Bitcoin transaction is confirmed within 10-30 minutes, but it can take longer during periods of high network activity.
Can I cancel a cryptocurrency transaction after it’s been sent?
Once a cryptocurrency transaction is broadcast to the blockchain network, it cannot be canceled. However, some wallets and services offer the ability to replace an unconfirmed transaction with a new one that includes a higher transaction fee, which can help prioritize the new transaction.
What happens if I send cryptocurrency to the wrong address?
If you send cryptocurrency to the wrong wallet address, the transaction is usually irreversible, and you may lose your funds. To avoid this, always double-check the recipient’s address before confirming the transaction.
Are cryptocurrency transactions taxable?
Cryptocurrency transactions may be subject to taxation, depending on your jurisdiction and the specific tax laws in place. It’s essential to consult with a tax professional to understand your obligations and ensure compliance with relevant tax regulations.
Can I send cryptocurrency using a credit or debit card?
Some services allow you to purchase and send cryptocurrency using a credit or debit card, but this is not the same as sending cryptocurrency directly from your wallet. When using a card, you’re typically using a third-party service that facilitates the transaction.