Table of Contents
A robot is an automated machine that can execute specific tasks with little or no human intervention. The field of robotics has seen remarkable advancements in the last 50 years. Robots can perform tasks better than humans in certain areas such as automating manual activities, working in hazardous environments, and assisting with surgeries. However, robots also have limitations, such as the inability to soothe scared patients or empathise with human emotions.
There are various types of robots, including androids, telechirs, telepresence robots, industrial robots, swarm robots, and smart robots. Each type has its own specific functions and applications. Robots have common characteristics, such as mechanical construction, electrical components, and computer programming.
Robotics technology, including robotic process automation (RPA) and intelligent process automation (IPA), has been driving digital transformation in various industries. The history of robots can be traced back to early designs by Leonardo da Vinci, and significant milestones include the invention of Unimate, the development of AI-based bots, and the introduction of autonomous machines like BigDog.
The future of robotics holds promising advancements in robot vision, learning, and navigation, and the use of AI for improving robotic capabilities.
Types of Robots and Their Applications
When it comes to robots, there is a wide range of types and applications to consider. Each type of robot serves a unique purpose and is designed to excel in specific areas. Let’s explore some of the most common types of robots and the applications they are used in.
1. Androids
Androids are humanoid robots that closely resemble humans. They have human-like features and are commonly used in a variety of fields, including:
- Caregiving: Androids can provide assistance and support to the elderly or individuals with disabilities.
- Search and Rescue: They can navigate challenging environments and aid in locating missing persons.
- Space Exploration: Androids are used to gather data and perform tasks in space missions.
- Entertainment: They are utilized in the entertainment industry, such as in movies and theme parks.
- Healthcare: Androids assist in medical procedures and can enhance patient care.
2. Telechirs and Telepresence Robots
Telechirs are remote-controlled robots that enable a sense of being present in dangerous or remote environments. They are often used in the following applications:
- Telepresence Systems: Telechirs provide a means for individuals to remotely participate in meetings and consultations.
- Business Consultations: They allow experts to provide guidance and support from afar, saving travel costs and time.
- Healthcare: Telepresence robots enable doctors to remotely examine and interact with patients, especially in rural or underserved areas.
- Home Monitoring: Individuals can monitor their homes and maintain a presence even when away.
3. Industrial Robots
Industrial robots are versatile manipulators that can be programmed for various applications. They are commonly used in industries to optimize processes and improve efficiency. Some of their key applications include:
- Process Optimization: Industrial robots enhance performance and productivity in manufacturing processes.
- Automation: They automate repetitive and hazardous tasks, reducing the risk of human errors and injuries.
- Safety Enhancement: Industrial robots can handle dangerous substances or operate in hazardous environments.
- Cost Reduction: By automating production, industrial robots help lower labor costs and increase overall efficiency.
4. Swarm Robots
Swarm robots are a group of robots that work collaboratively to accomplish complex tasks. These robots work under the supervision of a single controller and are used in various applications, including:
- Exploration: Swarm robots are deployed in exploratory missions, gathering data from multiple locations simultaneously.
- Surveillance: They can quickly cover large areas for surveillance purposes, such as monitoring wildlife or detecting threats.
- Construction: Swarm robots can work together to construct structures, making them efficient in construction sites.
- Disaster Recovery: They aid in disaster zone clearing and rescue operations, navigating through challenging environments.
5. Smart Robots
Smart robots are equipped with built-in artificial intelligence (AI) systems that allow them to learn from their environment and collaborate with humans. These robots find applications in various areas, including:
- Agricultural Labor: Smart robots assist in agricultural tasks, such as planting, harvesting, and monitoring crop health.
- Food Waste Management: They help automate sorting and recycling processes, reducing food waste and promoting sustainability.
- Marine Ecosystem Study: Smart robots are used to explore and study marine ecosystems, providing valuable data for research and conservation.
- Product Organization in Warehouses: They optimize warehouse operations by efficiently organizing and managing inventory.
As you can see, robots have diverse applications across various sectors, revolutionizing industries and improving our lives in countless ways.
| Type of Robot | Applications |
|---|---|
| Androids | Caregiving, Search and Rescue, Space Exploration, Entertainment, Healthcare |
| Telechirs and Telepresence Robots | Telepresence Systems, Business Consultations, Healthcare, Home Monitoring |
| Industrial Robots | Process Optimization, Automation, Safety Enhancement, Cost Reduction |
| Swarm Robots | Exploration, Surveillance, Construction, Disaster Recovery |
| Smart Robots | Agricultural Labor, Food Waste Management, Marine Ecosystem Study, Product Organization in Warehouses |
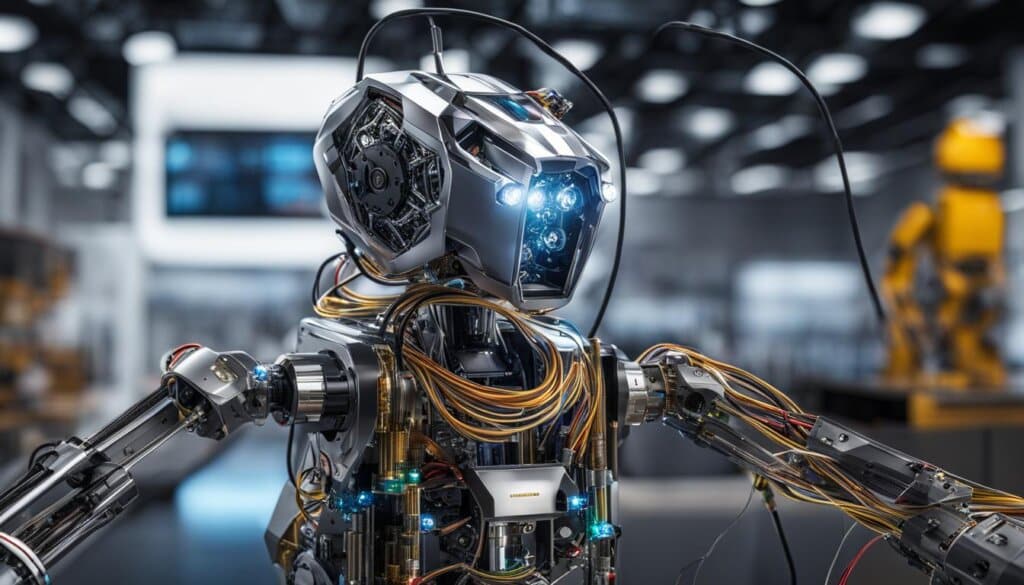
Components of a Robot
Robots are complex machines composed of various components that work together to perform their tasks efficiently. Each component plays a crucial role in enabling a robot to sense its environment, make decisions, and execute actions effectively. Here are the key components of a robot:
1. Control System
The control system serves as the brain of the robot. It includes a central processing unit (CPU) that directs the robot’s tasks at a high level. The control system receives input from sensors, processes the information, and sends signals to the actuators for movement or other actions. It is responsible for coordinating the robot’s overall functionality.
2. Sensors
Sensors allow the robot to perceive and interact with the surrounding world. They provide electrical signals that relay information to the control system. Common types of sensors used in robots include video cameras, photoresistors, microphones, proximity sensors, and force/torque sensors. By gathering data from the environment, sensors enable robots to make informed decisions and adapt to changes in their surroundings.
3. Actuators
Actuators are responsible for the physical movement and manipulation performed by the robot. They receive signals from the control system and convert them into mechanical actions. Motors are commonly used as actuators in robots, powering the robot’s limbs, wheels, or other moving parts. By actuating these components, the robot can perform tasks and interact with its environment.
4. Power Supply
The power supply is essential for providing energy to the robot’s components. It can be either an internal battery or an external power source, such as AC power from a wall outlet. The power supply ensures that the robot has sufficient electrical power to operate effectively during its tasks.
5. End Effectors
End effectors are external components that allow the robot to interact with objects and accomplish specific tasks. These components vary depending on the robot’s intended purpose. Examples of end effectors include paint sprayers, drilling tools, gripping claws, welding torches, or suction cups. The choice of end effector depends on the desired application and the manipulative capabilities required.
By combining these components, robots can perform a wide range of tasks, from simple actions to complex operations. The control system directs the robot’s actions, sensors provide environmental feedback, actuators enable movement, the power supply ensures energy supply, and end effectors facilitate task completion. These components work together seamlessly, allowing robots to operate efficiently and autonomously.
How Robots Function
Robots can function in different ways depending on their level of autonomy and interaction with humans. Independent robots are capable of functioning autonomously, carrying out tasks without human intervention. These robots can undertake dangerous, mundane, or impossible tasks, such as bomb diffusion, deep-sea travel, or factory automation. Dependent robots, on the other hand, interact with humans to enhance and supplement existing actions. An example of a dependent robot is an advanced prosthetic limb controlled by the human mind.
Robots function through a feedback loop, where sensors provide measurements to a controller or computer, which processes the information and sends control signals to actuators for movement. The level of autonomy in robots varies, with some controlled remotely by humans, some running autonomously without human intervention, and others relying on a combination of remote control and autonomous behavior.
| Type of Robot | Function |
|---|---|
| Independent Robots |
|
| Dependent Robots |
|
The Future of Robotics
The future of robotics holds immense potential for advancements in various areas. While there are challenges to overcome, such as the cost and complexity associated with robotics components, progress is being made at an accelerating rate. Integrating sensors, computers, actuators, software, and user interfaces can be a complex task, but advancements in robotics technology are paving the way for practical and capable robots in real-world environments.
Robot vision, learning, navigation, and AI are driving the advancements in robotics, enabling robots to perceive their surroundings, make informed decisions, and navigate complex environments. Furthermore, the development of hardware and software standards is improving interoperability among different robots, allowing them to seamlessly collaborate and share information. Robotics software, like the Robot Operating System, plays a crucial role in enabling robots to accomplish tasks effectively and efficiently.
Although practical home robots may still be a few years away, the future of robotics relies on the collective contribution of individuals. Those who are interested in robotics can become roboticists by getting involved in robotics clubs, competitions, courses, and research. By actively participating in robotics-related activities, individuals can contribute to the advancements in robotics and shape the future of this exciting field. As robotics continues to evolve and improve, the possibilities for robotic applications and their impact on everyday life will only increase.
FAQ
What is a robot?
A robot is an automated machine that can execute specific tasks with little or no human intervention.
What are the types of robots and their applications?
The types of robots include androids (used in caregiving, search and rescue, space exploration, entertainment, and healthcare), telechirs (used for telepresence in dangerous or remote environments), telepresence robots (used for business consultations, healthcare, and home monitoring), industrial robots (used for various applications to optimize process performance, automate production, enhance safety, and lower costs), swarm robots (work in groups to carry out complex tasks), and smart robots (have built-in AI systems for problem-solving in areas such as agriculture, marine ecosystem study, warehousing, and disaster zone clearing).
What are the components of a robot?
The components of a robot include the control system (CPU), sensors (video cameras, photoresistors, microphones), actuators (motors), power supply (internal battery or AC power), and end effectors (external components like paint sprayers, drills, or gripping claws).
How do robots function?
Robots can function independently (autonomously carrying out tasks without human intervention) or dependently (interacting with humans to enhance existing actions). They function through a feedback loop, where sensors provide measurements, a controller or computer processes the information, and control signals are sent to actuators for movement.
What does the future of robotics hold?
The future of robotics holds promising advancements in robot vision, learning, and navigation, as well as the use of AI for improving capabilities. While there are challenges such as cost and complexity, progress is being made at an accelerating rate. Robotics technology is driving digital transformation in various industries, and practical and capable robots in real-world environments are becoming a possibility.












