Table of Contents
A coaxial cable is a fundamental component of modern connectivity solutions. Its functions and relevance in various applications make it an essential wiring medium for transmitting high-frequency signals. From cable TV to internet connections, coaxial cables play a crucial role in ensuring reliable and efficient signal transmission.
Coaxial cables consist of several parts that work together to deliver superior performance. These include a center conductor, a dielectric insulator, one or more shields, and a protective jacket. The design of coaxial cables allows for minimal signal loss, making them ideal for long-distance transmissions.
Whether you’re connecting your television to a cable box, boosting cellular signals with a signal booster, or setting up a ham radio system, coaxial cables provide the necessary connectivity. Their ability to handle high-frequency signals and protect against interference ensures a seamless connection for various devices and systems.
There are different types of coaxial cables available, each with its own characteristics and applications. These include RG and LMR types, such as RG-6/U, RG-8, RG-11, RG-59, LMR200, LMR240, LMR400, and LMR600.
In summary, understanding the functions and applications of coaxial cables is essential in navigating the world of modern connectivity solutions. Whether you’re setting up a cable TV network or establishing a reliable internet connection, coaxial cables provide the necessary foundation for seamless signal transmission.
What Does a Coaxial Cable Look Like?
A coaxial cable is constructed using four main parts: the center conductor/core, the dielectric insulator, the shield(s), and the jacket. Let’s take a closer look at each component:
- Center Conductor/Core: The center conductor/core is a single copper or copper-coated steel wire that carries the RF signals. It is the innermost part of the coaxial cable and is responsible for transmitting the electrical signals.
- Dielectric Insulator: Surrounding the center conductor is the dielectric insulator, usually made of plastic. Its purpose is to maintain a constant distance between the center conductor and the next layer, providing insulation and preventing signal loss.
- Shield(s): The shield is the layer that wraps around the dielectric insulator. It is made of woven copper, aluminum, or other metals. The shield serves two main functions: protecting the inner layers from external electromagnetic interference and containing and reflecting the electrical signals within the cable.
- Jacket: The outermost layer of the coaxial cable is the jacket. This layer provides overall protection to the cable and indicates its installation rating. The jacket is typically made of durable and flexible materials to ensure the longevity and reliability of the cable.
Here’s a visual representation of a coaxial cable construction:
| Component | Image |
|---|---|
| Center Conductor/Core | |
| Dielectric Insulator | |
| Shield | |
| Jacket |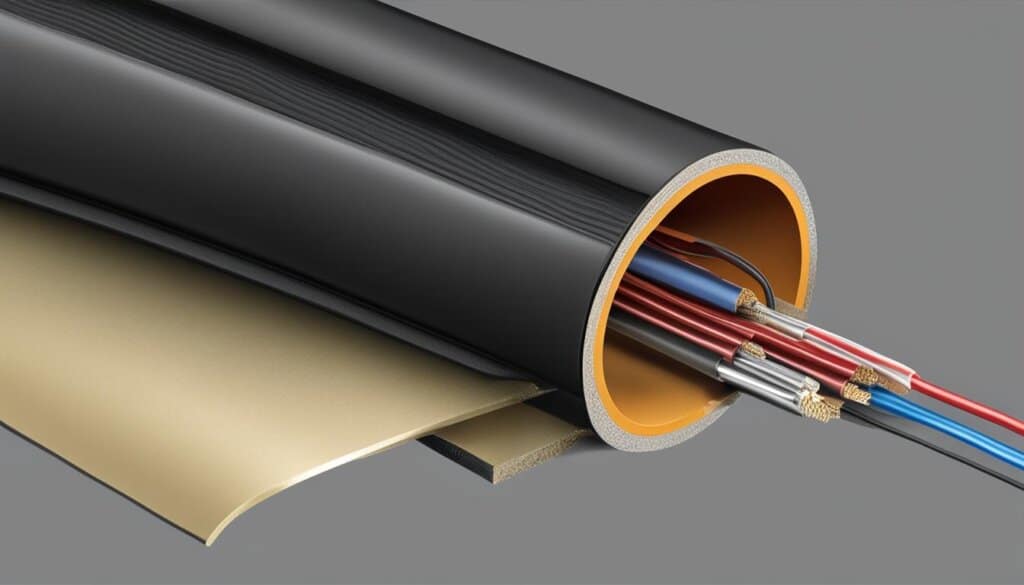  |
Understanding the construction of a coaxial cable is crucial to grasp how it works and appreciate its importance in various applications.
How Do Coaxial Cables Work?
Coaxial cables play a crucial role in ensuring the smooth transmission of signals. Understanding how these cables function is essential for grasping their importance in modern connectivity solutions. Let’s take a closer look at the inner workings of coaxial cables.
Signal Transmission
The core functioning of coaxial cables revolves around signal transmission. These cables enable the transfer of signals from one point to another with minimal loss, making them ideal for applications like cable TV, internet, and cell boosters. The signal travels through the center wire, also known as the core conductor, which acts as a pathway for the signal to travel.
The center conductor is surrounded by a dielectric insulator, usually made of plastic. This insulator serves two important purposes. It maintains a consistent distance between the core conductor and the outer shield, preventing the signals from coming into direct contact and canceling each other out. Additionally, the dielectric insulator prevents any signal leakage or interference, ensuring the integrity of the transmitted signal.
Electromagnetic Interference Protection
One of the key advantages of coaxial cables is their ability to protect against electromagnetic interference. An outer metal shield surrounds the dielectric insulator, acting as a barrier against external electromagnetic disturbances. This shield safeguards the transmitted signal from picking up unwanted noise or interference, ensuring clear and reliable signal transmission.
The combined effect of the core conductor, dielectric insulator, and metal shield allows coaxial cables to minimize signal loss and maintain signal quality even over long distances. This makes them an ideal choice for applications that require high-quality signal transmission, such as cable TV and broadband internet.
Visual Representation of Coaxial Cable Functioning
Here is a visual representation of how coaxial cables work:
| Components | Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Core Conductor | The central wire that carries the signal. |
| 2. Dielectric Insulator | A layer of non-conductive material that separates the core conductor from the shield. |
| 3. Metal Shield | Surrounds the dielectric insulator and provides protection against electromagnetic interference. |
As shown in the diagram above, the core conductor carries the signal, while the dielectric insulator maintains its distance from the outer shield. The metal shield acts as a protective barrier, ensuring the purity of the transmitted signal.
By understanding the functioning of coaxial cables, it becomes evident why they are widely used in various industries and applications where reliable signal transmission is critical.
Uses and Applications of Coaxial Cables
Coaxial cables play a crucial role in various applications, including cable TV, signal boosters, cable internet, ham radio, and RF systems. These cables are relied upon by cable operators, telephone companies, and internet providers for transmitting radio frequency signals. Let’s explore the diverse range of uses and applications of coaxial cables in more detail.
Cable TV
Coaxial cables are widely used in the cable television industry. They carry video and data signals from cable companies to televisions, providing high-quality television programming to households. The robust construction of coaxial cables ensures that the signal quality remains intact during transmission, delivering a seamless viewing experience.
Signal Boosters
For individuals experiencing weak cell phone signals, coaxial cables prove invaluable. Signal boosters, also known as cell phone boosters or amplifiers, utilize coaxial cables to enhance reception and improve call quality. These boosters amplify weak signals and rebroadcast them, allowing individuals to stay connected even in areas with poor signal strength.
Cable Internet
Cable internet service providers rely on coaxial cables to bring high-speed internet connectivity to homes and offices. Coaxial cables have the capacity to transmit large amounts of data, making them well-suited for carrying internet signals. By utilizing coaxial cables, cable internet service providers ensure that users can enjoy fast and reliable internet connections.
Ham Radio
Amateur radio enthusiasts, commonly known as ham radio operators, utilize coaxial cables for communication purposes. Coaxial cables are instrumental in transmitting and receiving radio signals, enabling ham radio operators to connect with others around the world. The high-performance capabilities of coaxial cables ensure efficient signal transmission and reception.
RF Systems
Coaxial cables are widely utilized in basic RF systems that require the transmission of radio frequency signals. These systems can include applications such as wireless communication, radar systems, automotive electronics, and more. Coaxial cables provide the necessary transmission medium to ensure accurate and reliable RF signal transmission within these systems.
As seen above, coaxial cables have an extensive range of uses and applications. They are integral in delivering cable TV programming, boosting weak cell phone signals, providing fast internet connectivity, facilitating ham radio communication, and enabling the transmission of RF signals within various systems.
Types of Coaxial Cables
When it comes to coaxial cables, there are various types available to suit different applications. These cables can be categorized into two main types: RG coax cables and LMR coax cables. Each type has its own unique characteristics and uses.
RG Coax Cables
RG coax cables refer to a series of cables named RG-6/U, RG-8, RG-11, and RG-59. These cables are widely used in different industries due to their specific features and benefits.
- RG-6/U: RG-6/U is commonly used for cable television and internet applications. It provides excellent signal transmission quality and is suitable for long-distance signal transfers.
- RG-8: RG-8 is mainly used in audio control rooms and radio antennas. It offers low signal loss and high conductivity, making it ideal for transmitting audio signals.
- RG-11: RG-11 is designed for applications such as CATV, HDTV, TV antennas, and video distribution. With its enhanced signal carrying capacity, it ensures high-quality video signals over significant distances.
- RG-59: RG-59 is commonly used in CCTV, audio video, and other low-frequency applications. It is cost-effective and suitable for short-distance signal transmissions.
LMR Coax Cables
LMR coax cables, including LMR200, LMR240, LMR400, and LMR600, provide greater flexibility, ease of installation, and lower cost compared to RG coax cables. These cables are widely used in various industries due to their unique advantages.
“LMR coax cables are popular for their flexibility, making them easy to work with during installations. They offer lower signal loss, allowing for better signal quality over long distances.”
LMR200 is commonly used in low-power and low-frequency applications, while LMR240 is suitable for short-run communication and RF applications. LMR400 is a versatile cable with a wide range of uses, including WLAN, Wi-Fi, GPS, and cellular applications. LMR600 is designed for high-power applications where signal loss must be minimized.
Having a clear understanding of the different types of coaxial cables available can help you choose the right cable for your specific application needs. Whether it’s for cable television, audio control rooms, CCTV, or high-power RF systems, selecting the appropriate coaxial cable ensures optimal performance and reliable signal transmission.
Coaxial Cable Signal Loss
Signal loss is an inevitable occurrence in coaxial cables, leading to potential degradation of the transmitted signals. It is measured in decibels (dB), which represents the weakening of the signal as it travels through the cable. To maximize signal quality, it is important to understand the concept of signal loss and its impact on different coaxial cable types.
Different coaxial cables have varying levels of signal loss per 10 feet, which can directly affect the performance of the system. Let’s explore some commonly used coaxial cable types and their respective signal loss characteristics:
| Coaxial Cable Type | Signal Loss per 10ft (dB) |
|---|---|
| Wilson400 | 0.54 |
| RG-11 | 0.6 |
| RG-6 | 1.5 |
| RG-174 | 6.4 |
From the table above, we can observe that the Wilson400 and RG-11 coaxial cables have the least signal loss per 10ft, making them more effective for home installations where longer cable lengths are required. On the other hand, the RG-6 and RG-174 cables may experience higher signal loss, requiring careful consideration when planning and setting up a coaxial cable network.
It is worth noting that the RG-174 coaxial cable is particularly unsuitable for installations requiring more than 6 feet of cable. This is due to its poor signal-carrying capabilities, making it less suitable for applications that demand reliable and long-distance signal transmission.
Matching Impedance and Calculating Signal Loss
Impedance is an important consideration when dealing with coaxial cables. It refers to the opposition of the cable to the flow of electrical energy and is usually measured in Ohms (Ω). Proper impedance matching helps minimize signal loss and maximize signal transfer efficiency.
When planning a coaxial cable installation, it is essential to calculate the expected signal loss based on the length and cable characteristics. Online calculators or formulas can help estimate the signal loss in a specific coaxial cable setup, taking into account factors such as cable type, length, and frequency.
To ensure optimal signal performance, consider the signal gain and potential signal loss throughout the coaxial cable network. This information will help in selecting the most suitable cable type and ensuring the integrity of the transmitted signals.
Important Coaxial Cable Features to Consider Before You Buy
When purchasing a coaxial cable, it is crucial to take into account several important features to ensure optimal performance and suitability for your specific needs. These features include cable length, thickness, impedance, shielding, and characteristic impedance.
Cable Length and Thickness
The length and thickness of a coaxial cable are essential factors to consider. Coaxial cables come in various lengths, ranging from a few feet to hundreds of feet, to accommodate different installation requirements. Similarly, the thickness or gauge of the cable affects its durability and signal transmission capabilities. Thicker cables are generally more robust and can carry signals over longer distances without significant signal loss.
Impedance
Impedance is a critical characteristic of coaxial cables that determines their electrical resistance to the flow of energy. It plays a vital role in maintaining optimal signal integrity and reducing signal loss. The most common impedance value for coaxial cables is 75 ohms, which is suitable for most residential applications such as cable television and internet connections. However, higher impedance values are also available to meet specific requirements.
Shielding
Shielding is an integral feature of coaxial cables to protect against electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference (RFI). The shielding is usually made of a conductive material like copper or aluminum, and it surrounds the core conductor and insulating layer to prevent interference from external sources. The effectiveness of the shielding directly impacts the quality of the transmitted signal, making it crucial to choose a cable with adequate shielding for your specific application.
Characteristic Impedance
Characteristic impedance is a fixed value that determines how a signal propagates through a coaxial cable. It is an important factor to consider when connecting devices or components that require a specific impedance match for optimal signal transfer. The characteristic impedance of a cable should align with the impedance requirements of the devices or systems it will be connected to, ensuring proper signal transmission without reflections or signal loss.
| Cable Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Cable Length | The physical length of the coaxial cable, usually in feet or meters. |
| Cable Thickness | The gauge or thickness of the coaxial cable, affecting its durability and signal transmission capabilities. |
| Impedance | The electrical resistance of the cable to energy flow, influencing signal integrity and loss. |
| Shielding | The protective layer surrounding the core conductor and insulator to prevent electromagnetic and radio frequency interference. |
| Characteristic Impedance | The fixed value that determines signal propagation through the cable and compatibility with connected devices. |
Considering these important coaxial cable features before making a purchase will help ensure that you select a cable that meets your specific needs and provides reliable and high-quality signal transmission.
Interference Issues with Coax and Types of Connectors
Coaxial cables, despite their many advantages, can sometimes face interference problems that affect signal quality. One common issue is signal leakage, where the RF signals escape through small gaps or damaged areas in the cable’s insulation. This can result in reduced signal strength and performance. To mitigate interference and maintain signal integrity, it is crucial to use coaxial cables with smooth conductive shields that prevent signal leakage and external interference.
In certain sensitive environments like nuclear reactors or high-security facilities, additional measures may be required to minimize interference. These can include using specialized coaxial cables with enhanced shielding capabilities to protect against external electromagnetic fields and prevent signal corruption. These advanced cables are designed to maintain consistent signal quality even in challenging environments.
When it comes to connecting coaxial cables to devices, choosing the right type of connector is equally important. There are several types of coaxial cable connectors available, each designed for specific applications and requirements. Popular connectors include BNC, TNC, SMA, SMB, QMA, RCA, and F connectors. These connectors ensure a secure and reliable connection, catering to different needs ranging from television and video signals to telecommunications and industrial hardware.
For example, BNC connectors are commonly used in video and RF applications, while TNC connectors are preferred for wireless communication and military applications. SMA connectors are widely utilized in high-frequency applications, and SMB connectors are commonly found in cable modems and Ethernet networks. QMA connectors offer quick and easy connections, making them suitable for a wide range of equipment. RCA connectors are often used in audio and video applications, while F connectors are predominantly used in cable TV and satellite TV installations.
FAQ
What is a coaxial cable?
A coaxial cable is an electrical transmission line used to carry high radio frequency (RF) signals with minimal signal loss. It is widely used in applications such as phone lines, cable TV, internet, and cell boosters.
What does a coaxial cable look like?
A coaxial cable consists of four main parts: the center conductor/core, the dielectric insulator, the shield(s), and the jacket. The center conductor is a single copper or copper-coated steel wire, surrounded by a dielectric insulator made of plastic. The shield, made of woven copper, aluminum, or other metals, wraps around the insulator. The outer jacket provides overall protection and indicates the cable’s installation rating.
How do coaxial cables work?
Coaxial cables work by transmitting signals through the center wire while using a metal shield to ensure signal quality and protect against electromagnetic interference. The distance between the core and shield is maintained by the dielectric insulator, which also prevents the signals from coming in contact and canceling each other. The outer jacket provides insulation and protects the components from damage.
What are the uses and applications of coaxial cables?
Coaxial cables are widely used in various applications, including cable TV, signal boosters, cable internet, ham radio, and RF systems. They are essential for carrying video and data signals, providing cable internet, enabling ham radio communication, and carrying RF signals in basic RF systems.
What are the types of coaxial cables?
There are different types of coaxial cables available, categorized as RG and LMR types. RG coax cables include RG-6/U, RG-8, RG-11, and RG-59, each with specific characteristics and uses. LMR coax cables, such as LMR200, LMR240, LMR400, and LMR600, provide greater flexibility, ease of installation, and lower cost compared to RG coax cables.
What is the signal loss in coaxial cables?
Signal loss is an inevitable occurrence in coaxial cables and is measured in decibels (dB). Different coaxial cables have varying levels of signal loss per 10 feet. For example, the Wilson400 and RG-11 have the least loss per 10ft, making them more effective for home installations compared to the RG-6. The RG-174 is not suitable for installations requiring more than 6 feet of cable as it poorly carries signals.
What features should I consider before buying a coaxial cable?
Before buying a coaxial cable, it is important to consider its length, thickness, impedance, shielding, and characteristic impedance. Coaxial cables come in various lengths and thicknesses, suitable for different applications. The impedance, shielding, and characteristic impedance affect the cable’s performance and suitability for specific needs.
What interference issues can coaxial cables experience and what types of connectors are available?
Coaxial cables can experience issues such as signal leakage and outside interference penetrating the insulation. Using smooth conductive shields and special shielding can help reduce interference. There are different types of coaxial cable connectors available, including BNC, TNC, SMA, SMB, QMA, RCA, and F connectors. These connectors have specific uses and are appropriate for different applications, ensuring proper connectivity and signal transmission.