Table of Contents
The study of matter and its composition, structure, properties, transformations from one form to another, and the energy that accompanies its transformation is known as chemistry. Chemistry is a branch of science that focuses on the systematic study of matter. It is one of the several disciplines in the field of science, which also include biology, physics, anatomy, geology, and ecology.
Chemistry delves into the fundamental makeup of matter, exploring its composition, structure, and properties, as well as the various transformations it can undergo. In essence, chemistry seeks to understand what all matter is made of and how it behaves.
By investigating the composition of matter, scientists can uncover the building blocks that make up everything in the universe. Understanding the structure and properties of matter allows us to comprehend the diverse range of materials and substances that exist, from the tiniest atoms to complex molecules and beyond.
Throughout history, countless scientists have dedicated their lives to unraveling the secrets of matter’s composition. Their discoveries and theories have paved the way for technological advancements, from the development of new materials to breakthroughs in medicine and energy.
In the following sections, we will explore the branches of science, the structure of atoms, the evolution of atomic theory, and delve into the fascinating world of matter’s composition.
Branches of Science
Science encompasses a wide range of disciplines, each devoted to exploring specific areas of scientific study. Some notable branches of science include:
- Biology: Biology focuses on the study of living organisms and their function. It explores the intricate processes and structures that enable life to exist and thrive.
- Physics: Physics examines the fundamental laws and principles that govern the universe. It delves into the nature of matter, energy, motion, and the forces that shape our world.
- Anatomy: Anatomy is the branch of science that investigates the structure of living organisms. It explores the various systems and organs within the human body, as well as the anatomy of other animals.
- Geology: Geology explores the Earth’s structure, composition, and history. It studies the rocks, minerals, fossils, and processes that have shaped our planet over millions of years.
- Ecology: Ecology investigates the relationships between organisms and their environment. It examines the interconnectedness and interdependence of living organisms, as well as the effects of human activity on ecosystems.
These branches of science contribute to our understanding of the world around us and provide insights into the various components of matter.
The Structure of Atoms
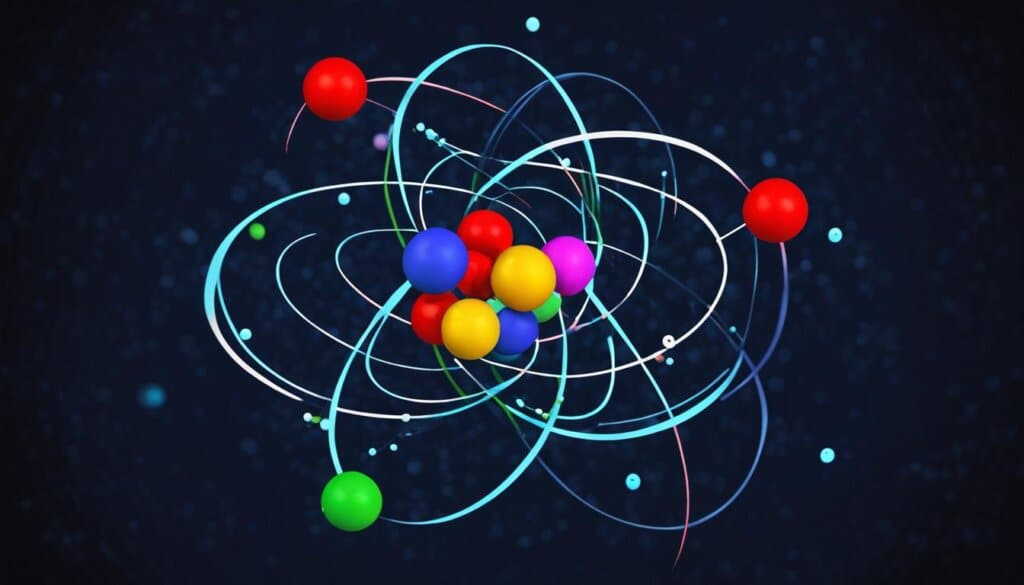
At the heart of understanding the composition of matter is the structure of atoms. Atoms are the basic building blocks of matter, composed of subatomic particles. The structure of an atom consists of a central nucleus, which contains protons (positively charged particles) and neutrons (particles with no electrical charge). The nucleus is surrounded by a cloud of electrons (negatively charged particles). The electrons occupy regions of space known as energy levels or electron shells. The number and arrangement of these subatomic particles determine the properties of an atom and the element it represents.
Protons carry a positive charge equal in magnitude to the negative charge of electrons, resulting in electrically neutral atoms. Neutrons have no electrical charge. Together, the protons and neutrons account for almost all of the mass of an atom, while the electrons occupy a relatively large volume of empty space within the atom.
| Subatomic Particle | Charge | Location |
|---|---|---|
| Protons | Positive (+) | Nucleus |
| Neutrons | No charge | Nucleus |
| Electrons | Negative (-) | Energy levels or electron shells surrounding the nucleus |
The Evolution of Atomic Theory
Throughout history, the understanding of the composition of matter has evolved through the development of atomic theory. Ancient Greek atomistic philosophers, such as Leucippus and Democritus, proposed that all matter was composed of small, indivisible particles called atoms. This idea laid the foundation for further exploration of matter’s composition.
In the 19th century, John Dalton revolutionized chemistry with his atomic theory, which posited that matter consists of tiny particles called atoms and explained various properties and behaviors of matter. Dalton’s theory outlined that atoms are indivisible and combine in specific ratios to form compounds. This breakthrough in understanding matter composition paved the way for advancements in the field of chemistry.
Building on Dalton’s work, J.J. Thomson’s experiments with cathode ray tubes led to the discovery of the electron, a subatomic particle found in atoms. Thomson’s findings challenged the notion of atoms being indivisible and provided crucial insights into the structure of matter. Later on, Robert Millikan’s oil drop experiment accurately determined the charge of the electron, further refining the understanding of atomic structure.
The evolution of atomic theory, from the philosophical ideas of ancient Greek atomistic philosophers to the groundbreaking experiments of Dalton, Thomson, and Millikan, has played a crucial role in unraveling the mysteries of matter’s composition. It has provided scientists with the knowledge to explore the fundamental building blocks of our world and understand the intricate nature of atoms.
FAQ
What is chemistry?
Chemistry is the study of matter and its composition, structure, properties, and transformations. It focuses on understanding what all matter is made of and how it behaves.
What are the branches of science?
The branches of science include biology, physics, anatomy, geology, and ecology. Each branch explores specific areas of scientific study and contributes to our understanding of the world and matter.
What is the structure of atoms?
Atoms are the basic building blocks of matter. They have a central nucleus that contains protons and neutrons, which are surrounded by a cloud of electrons. The number and arrangement of these subatomic particles determine the properties of an atom and the element it represents.
How has atomic theory evolved?
Throughout history, atomic theory has evolved through the contributions of various scientists. Ancient Greek atomistic philosophers proposed the idea of atoms, and John Dalton’s atomic theory revolutionized chemistry. J.J. Thomson discovered electrons, and Robert Millikan further explored their properties. The evolution of atomic theory has played a crucial role in understanding the composition of matter.







