Table of Contents
In the world of wireless communication, technological advancements are constantly improving our connectivity and enhancing our digital experiences. One such breakthrough is Orthogonal frequency-division multiple access (OFDMA) technology, which plays a crucial role in the latest incarnation of wireless networks, Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax).
OFDMA is a transmission technique that allows access points to serve multiple clients simultaneously, revolutionizing the way data is transmitted over Wi-Fi networks. This technology is based on orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM), which utilizes multiple subcarriers within the same communications channel to efficiently transfer data.
Unlike traditional methods, OFDMA is a multi-user variant of OFDM, enabling access points to establish connections with multiple clients and facilitate simultaneous data transmission. This approach significantly improves spectral efficiency, ensuring that the available bandwidth is utilized optimally.
By upgrading both frequency-division multiplexing (FDM) and OFDM, OFDMA offers higher efficiency and capacity in wireless communication systems. Its impact is particularly noteworthy when it comes to serving multiple clients efficiently and reliably.
How OFDMA Works
Orthogonal frequency-division multiple access (OFDMA) is a key technology in Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax) that enables efficient and simultaneous data transmission for multiple users. It achieves this through the use of subcarriers and resource units (RUs) to allocate the available bandwidth effectively.
Subcarriers are closely spaced carrier signal waves that carry small bits of information. These subcarriers allow for a streamlined data transmission process within the OFDMA system.
The channel is divided into smaller frequencies known as resource units (RUs). This division ensures the efficient use of the available bandwidth by assigning specific RUs to users based on their data requirements, quality of service needs, and device constraints.
With the allocation of RUs, OFDMA enables simultaneous communication with multiple users, maximizing the channel capacity. This feature is crucial for environments with high user density, such as crowded public spaces or enterprise networks.
OFDMA ensures strong connections, uninterrupted access, and lower latency for real-time applications like audio/video conferencing and online gaming.
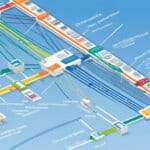
To understand how OFDMA works in Wi-Fi 6, take a look at the infographic below:
Figure 1: Infographic illustrating the functioning of OFDMA in Wi-Fi 6.
Advantages and Disadvantages of OFDMA
OFDMA, or Orthogonal Frequency-Division Multiple Access, offers several advantages and disadvantages in wireless communication systems. Understanding these pros and cons is crucial for optimizing network performance and spectral efficiency.
Advantages of OFDMA
- Intracell Interference: One of the main advantages of OFDMA is its resistance to intracell interference. By effectively managing multiple subcarriers, OFDMA improves signal quality and ensures reliable data transmission.
- Diversity Frequency: OFDMA enables higher diversity frequency by packing multiple subcarriers within the available bandwidth. This packed configuration allows for more efficient data transmission and utilization of the channel capacity.
- Flexibility in Channel Allocation: With OFDMA, resource units can be dynamically assigned based on user data requirements, quality of service, and device constraints. This flexibility optimizes channel allocation and ensures efficient communication for multiple users simultaneously.
- Better Coverage: OFDMA enhances spectral efficiency, improving coverage and range of wireless networks. This leads to stronger connections and broader access for users across different areas.
Disadvantages of OFDMA
- Intercell Interference: While OFDMA is resistant to intracell interference, it is somewhat prone to intercell interference. This interference can affect signal quality and overall network performance. Techniques like packet scheduling, frequency reuse, and interference coordination can help mitigate intercell interference and optimize performance.
- Complex Subcarrier Assignment: The complexity of subcarrier assignment in OFDMA can pose challenges in network optimization. Efficiently allocating subcarriers requires careful planning and management to ensure optimal spectral efficiency.
- Additional Power Requirements: OFDMA may require additional power to support the simultaneous transmission of multiple users. This increased power consumption can impact the overall power efficiency of wireless systems.
- Higher Sensitivity to Frequency Offset: OFDMA systems are more sensitive to frequency offset compared to other communication technologies. This sensitivity can affect the accuracy of data transmission and the overall performance of the network.
Despite the drawbacks, OFDMA is widely adopted in wireless LAN (Wi-Fi), LTE (4G), and WiMAX systems due to its numerous advantages in improving spectral efficiency and supporting simultaneous communication with multiple users.
Next, we will explore the implementation of OFDMA in Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax) and its impact on network capacity and power efficiency.
OFDMA in Wi-Fi 6
OFDMA, or orthogonal frequency-division multiple access, is a crucial technology enhancement introduced in Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax). With significantly higher speeds and network capacity than its predecessor Wi-Fi 5, Wi-Fi 6 revolutionizes wireless communication.
One of the key advantages of OFDMA is its ability to increase network capacity, addressing access issues that arise when multiple devices are active on a single network. By efficiently allocating resources and enabling simultaneous communication, OFDMA ensures strong connections, lower latency, and improved power efficiency for Wi-Fi-enabled devices.
Wi-Fi 6 not only offers better device scalability but also brings numerous benefits to enterprise networks, real-time applications, and mobile devices. With its improved network capacity, Wi-Fi 6 provides maximum throughput, enabling faster and more reliable data transmission.
In addition to improving network capacity, OFDMA in Wi-Fi 6 also contributes to power efficiency. By efficiently utilizing available resources and effectively managing simultaneous connections, Wi-Fi 6 devices can optimize power usage, enhancing battery life and reducing energy consumption.
FAQ
What is OFDMA?
OFDMA stands for Orthogonal Frequency-Division Multiple Access. It is a technology used in Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax) that allows access points to serve multiple clients simultaneously.
How does OFDMA work?
OFDMA is based on orthogonal frequency-division multiplexing (OFDM), which uses multiple subcarriers within the same communications channel. The channel is split into smaller frequencies called resource units (RUs), allowing efficient use of the available bandwidth. RUs are assigned to users based on their data requirements and other factors like quality of service and device constraints. This allocation enables simultaneous communication with multiple users, effectively using the channel capacity.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of OFDMA?
One of the main advantages of OFDMA is its resistance to intracell interference, leading to improved signal quality. However, it is somewhat prone to intercell interference, which can affect signal quality. Techniques like packet scheduling, frequency reuse, and interference coordination can mitigate intercell interference. OFDMA offers higher diversity frequency, efficient packing of subcarriers, flexibility in channel allocation, and better coverage. Potential disadvantages include the complexity of subcarrier assignment, additional power requirements, and higher sensitivity to frequency offset.
How is OFDMA used in Wi-Fi 6?
OFDMA is one of the key technology enhancements introduced in Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax). Wi-Fi 6 offers significantly higher speeds and network capacity compared to previous standards like Wi-Fi 5. OFDMA increases network capacity, mitigating access issues when multiple devices are active on a single network. It ensures strong connections, lower latency, and improved power efficiency for Wi-Fi-enabled devices. Wi-Fi 6 allows for better device scalability and offers benefits for enterprise networks, real-time applications, and mobile devices.