Table of Contents
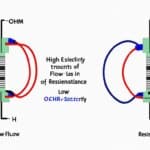
The ohm symbol plays a vital role in the world of electronics and electrical circuits. It represents the unit of electrical resistance in the International System of Units (SI). Understanding the ohm symbol and its significance is fundamental to comprehending the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance in electronic systems.
The ohm symbol itself is represented by the Greek letter omega (Ω). This symbol is used to denote the amount of resistance between two points in a conductor when a constant potential difference of one volt (V) produces a current of one ampere (A). By using the ohm unit, engineers and technicians can accurately measure and express resistance in a circuit.
Resistance, measured in ohms, is a fundamental property of materials and components in electronics. It determines how a material or component limits the flow of electric current. An understanding of resistance allows for designing and troubleshooting electronic systems effectively.
When calculating resistance in direct current (DC) circuits, Ohm’s Law is a key principle to consider. Ohm’s Law states that voltage (V) equals current (I) multiplied by resistance (R). This formula allows engineers to determine resistance by dividing the known voltage by the current.
In alternating current (AC) circuits, resistance alone is not sufficient to calculate impedance. AC circuits involve other factors, such as reactance, which is a combination of inductance and capacitance. Impedance, incorporating both resistance and reactance, is used to measure the total opposition to current flow in an AC circuit.
By understanding the ohm symbol, electrical resistance, and the principles of Ohm’s Law, engineers and technicians can effectively analyze, design, and troubleshoot electronic circuits. This knowledge is crucial for maintaining efficient and reliable electronic systems.
The Calculation of Resistance in DC Circuits
In a direct current (DC) circuit, the calculation of resistance is essential in understanding the behavior of electrical components. By using Ohm’s Law, we can determine the resistance based on the voltage and current in the circuit.
Ohm’s Law: V = IR
Where V represents the voltage, I represents the current, and R represents the resistance.
Let’s consider an example to illustrate the calculation of resistance:
A circuit contains a 9V battery and a current of 0.5A flowing through it. To find the resistance, we can use the formula R = V/I. By substituting the given values, we get:
R = 9V/0.5A = 18 ohms
The resistance of the circuit is 18 ohms.
Resistance in DC circuits arises from various factors, including components such as lightbulbs and conductors like copper wire. Understanding the resistance allows us to analyze the behavior of these components and ensure the optimal functioning of the circuit.
To further enhance your understanding of resistance calculation in DC circuits, refer to the table below, which provides a comprehensive summary of the key relationships between voltage, current, and resistance:
| Voltage (V) | Current (I) | Resistance (R) |
|---|---|---|
| Increasing | Remains constant | Increasing |
| Remains constant | Increasing | Decreasing |
| Decreasing | Remains constant | Decreasing |
By referring to the table and applying Ohm’s Law, you can easily calculate the resistance in different DC circuits.
Now that we have explored the calculation of resistance in DC circuits, let’s move on to understanding resistance calculation in AC circuits in our next section.
The Calculation of Resistance in AC Circuits
When it comes to alternating current (AC) circuits, resistance is just one piece of the puzzle. Unlike in DC circuits, AC circuits feature additional components that impact the flow of current, such as reactance, which is the combined effect of inductance and capacitance. In these circuits, impedance, a measure of the overall opposition to current flow, is used instead of resistance.
Impedance incorporates both resistance and reactance, providing a comprehensive view of the circuit’s resistance to current flow. To calculate impedance, you can use the formula Z = √(R^2 + X^2), where Z represents impedance, R represents resistance, and X represents reactance.
With the value of impedance determined, modified versions of Ohm’s Law can be employed to calculate the voltage and current in AC circuits. Since AC circuits involve dynamic changes in voltage and current direction, the inclusion of reactance in impedance calculations is crucial for accurate predictions and analysis.
By understanding how resistance, reactance, capacitance, and inductance combine to form impedance, engineers and technicians can make precise calculations for AC circuits. This knowledge enables them to design and troubleshoot complex systems, ensuring optimal performance and efficiency.
FAQ
What does the ohm symbol represent in electronics?
The ohm symbol is the standard unit of electrical resistance in the International System of Units (SI). It represents the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance in an electrical circuit.
How is resistance measured?
Resistance is measured in ohms. The ohm is defined as the amount of resistance between two points in a conductor when a constant potential difference of one volt (V) produces a current of one ampere (A). Ohms can be expressed in power-of-10 multiples, such as kiloohms (1,000 ohms) and megaohms (1,000,000 ohms).
How can resistance be calculated in a direct current (DC) circuit?
Resistance in a DC circuit can be calculated using Ohm’s Law. Ohm’s Law states that voltage equals current multiplied by resistance. This means that if the voltage and current in a circuit are known, the resistance can be calculated by dividing the voltage by the current. The formula for Ohm’s Law is V = IR, where V is voltage, I is current, and R is resistance.
What factors can cause resistance in a circuit?
Resistance in a circuit can be caused by various factors, including components like lightbulbs and conductors like copper wire.
What is the calculation for resistance in an AC circuit?
In an AC circuit, impedance is used instead of resistance. Impedance is a measure of the total opposition to current flow in a circuit and includes both resistance and reactance. The formula for calculating impedance is Z = √(R^2 + X^2), where Z is impedance, R is resistance, and X is reactance.