Table of Contents
Network segmentation is an essential aspect of modern network infrastructure. It involves dividing a larger physical network into smaller virtual networks, known as VLANs (Virtual LANs). VLANs offer numerous benefits, including improved network efficiency, enhanced security, and simplified network management.
By isolating broadcast domains, VLANs reduce network congestion and maximize network efficiency. This segmentation also provides a significant boost to network security by isolating subnetworks and enabling the implementation of tailored cybersecurity measures.
Furthermore, VLANs enable easier network management and scalability. With VLANs, network administrators can manage resources more effectively and scale the network infrastructure as required. Additionally, VLANs reduce the scope of compliance by allowing auditing on specific subnets rather than the entire network.
What is Network Segmentation?
Network segmentation is the practice of compartmentalizing a network according to firewall rules. It involves dividing a computer network into subnetworks or subnets, which work independently and in isolation. This practice helps in better management, security, and efficiency of the network.
Network segmentation can be achieved through various methods, including:
- Subnets: Dividing the network into smaller subnets based on IP addresses.
- Firewall segmentation: Using firewall rules to separate different parts of the network.
- SDN segmentation: Implementing Software-Defined Networking to create virtual networks within the physical network infrastructure.
By implementing network segmentation, organizations can effectively control access to sensitive data, minimize the impact of security breaches, and optimize network performance.
“Network segmentation is like dividing a large city into separate neighborhoods, each with its own security measures and rules. This way, if an unfortunate incident occurs in one neighborhood, it doesn’t affect the rest of the city.”
The Benefits of Network Segmentation
Network segmentation offers several advantages for organizations:
- Enhanced Security: By dividing the network into smaller segments, organizations can create separate security zones, allowing for stricter access controls. In the event of a security breach, the impact can be limited to a specific segment, minimizing the risk to the entire network.
- Improved Performance: Network segmentation reduces network congestion by isolating traffic within specific segments. This results in faster data transfer and better overall network performance.
- Easier Management: With network segmentation, administrators can apply specific policies and configurations to different segments, making it easier to manage and troubleshoot network issues.
- Scalability: As organizations grow, network segmentation allows for easier expansion without disrupting the entire network. New segments can be added or modified as needed without affecting existing infrastructure.
Implementing Network Segmentation
When implementing network segmentation, careful planning is crucial. It is important to define the desired segments, determine the appropriate firewall rules, and ensure network devices are properly configured.
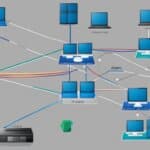
A detailed diagram of the network architecture, including the physical and logical layout, can help in visualizing the segmentation strategy. It is also important to regularly review and update the firewall rules and network segmentation configuration to adapt to changing security requirements.
| Segment | Features | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Data Center Segment | High-performance servers, storage, and networking devices | Business-critical applications, cloud environments |
| Guest Network Segment | Restricted access, limited bandwidth | Guest WiFi, visitors’ devices |
| IoT Segment | Connected devices, sensors, and gateways | Smart home devices, industrial automation systems |
| Workstation Segment | Desktops, laptops, and peripherals | Employee workstations, productivity tools |
What is VLAN?
VLAN or Virtual LAN is a type of network segmentation approach where the main physical network is divided into multiple smaller virtual networks. This division is done logically or virtually, without requiring additional physical resources. VLANs provide benefits like broadcast domain isolation, enhanced security, better network management, flexibility in scalability, and reduced scope of compliance. VLANs function at Layer 2 of the OSI model and can be configured at the switch level.
By implementing VLANs, organizations can logically divide a network into separate segments, each with its own characteristics, security policies, and access controls. It allows for the creation of logical divisions within a network, enabling better organization and control of network traffic. VLANs effectively isolate traffic within specific groups, departments, or locations, improving network security by restricting unauthorized access to sensitive information.

One of the key advantages of VLANs is broadcast domain isolation. Instead of all devices on a network receiving broadcast messages, VLANs limit the scope of broadcast traffic only to devices within the same virtual LAN. This helps in reducing network congestion and improving overall network performance and efficiency.
VLANs also offer enhanced network management capabilities. By logically grouping devices based on their function, VLANs simplify the management of network resources. IT administrators can easily configure and monitor VLANs at the switch level, making it easier to allocate bandwidth, control access, and troubleshoot network issues.
Furthermore, VLANs provide flexibility when it comes to network scalability. As an organization grows, VLANs can be easily expanded or reconfigured to accommodate new devices or departments. This logical division allows for seamless integration and expansion without the need for major changes to the network’s physical infrastructure.
“VLANs provide a logical and efficient way to segment a network, ensuring improved security, easier management, and optimal performance.” – Network Administrator, ABC Company
Benefits of VLAN:
- Enhanced network security and access control
- Broadcast domain isolation and reduced network congestion
- Better network management and resource allocation
- Flexibility in network scalability and expansion
- Reduced scope of compliance audits
How VLANs are Configured:
VLANs can be configured at the switch level using different methods, including:
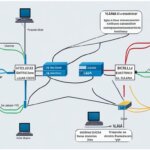
- Port-based VLANs: In this method, each switch port is assigned to a specific VLAN, allowing devices connected to that port to belong to the same virtual network.
- 802.1Q VLAN tagging: This method allows for the identification and segregation of VLAN traffic by adding a VLAN tag to the Ethernet frame. The VLAN tag includes information about the VLAN to which the frame belongs.
- VLAN membership by MAC address: With this method, devices are assigned to VLANs based on their MAC addresses. When a device connects to the network, the switch identifies its MAC address and assigns it to the appropriate VLAN.
Overall, VLANs offer significant benefits in terms of network security, management, and scalability. By logically dividing a network into smaller virtual networks, VLANs provide a flexible and efficient solution for network segmentation and logical division.
Differences between Network Segmentation and VLAN
In the realm of network architecture, network segmentation and VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network) play pivotal roles in dividing networks to enhance efficiency, security, and management. While both approaches aim to achieve network division, they differ in several aspects.
Network Segmentation – Subnetting
Network segmentation, often achieved through subnetting, involves dividing the network at the IP level. This process creates independent subnets, each with its own unique IP address. Subnets provide a logical division that allows for efficient management of network resources and improved security through access control.
Subnetting, also referred to as Layer 3 division, operates at the network layer (Layer 3) of the OSI model, utilizing IP addresses to segregate network traffic. By assigning IP addresses to specific subnets, network administrators can control the flow of data and optimize network performance.
VLAN – Layer 2 Division
VLAN, on the other hand, divides the network at the data link layer (Layer 2). It creates separate virtual networks within the same physical network, enabling logical isolation and enhanced network flexibility. VLANs provide a mechanism for grouping devices based on shared requirements, irrespective of their physical location.
Operating at Layer 2 of the OSI model, VLANs utilize tagging to identify and segregate network traffic. This allows for more efficient network management and the ability to prioritize traffic based on specific requirements or policies.
Configuration, Terminology, and Functionality
Network segmentation, through subnetting, typically involves configuration at the router level and requires knowledge of IP addressing, subnet masks, and routing protocols. VLAN configuration, on the other hand, takes place at the switch level, utilizing the concept of virtual LANs.
The terminology used in network segmentation revolves around IP addressing, subnets, and routers. In contrast, VLANs are characterized by VLAN IDs, trunk ports, and access ports, which define membership to specific virtual networks.
Functionally, network segmentation focuses on dividing networks based on IP addresses and routing protocols, allowing for the creation of independent subnets. VLANs, on the other hand, provide logical division based on virtual networks, enabling devices to communicate as if they were on the same physical network.
Visual Representation
| Aspect | Network Segmentation | VLAN |
|---|---|---|
| Division Level | Layer 3 (IP Level) | Layer 2 (Data Link Level) |
| Configuration Level | Router | Switch |
| Terminology | IP Addressing, Subnets, Routers | VLAN IDs, Trunk Ports, Access Ports |
| Functionality | Independent Subnets | Logical Division, Virtual Networks |
The visual representation above highlights the key differences between network segmentation and VLANs, including the division level, configuration level, terminology, and functionality.
Understanding these distinctions is crucial for network administrators in selecting the appropriate approach based on their network requirements, such as the need for IP-level division or logical isolation at the data link level.
When to Adopt Subnets and VLANs?
When it comes to dividing and managing networks, two key approaches stand out: subnets and VLANs. The choice between them depends on the specific network requirements and considerations. Subnets are ideal when there is a need to divide different networks at the IP level, allowing for the creation of multiple IP addresses for each partition. This enables efficient control over access to specific sub-networks, whether for internal or external connectivity.
On the other hand, VLANs are suitable for creating isolated networks within a single physical network. By operating at the data link level, VLANs prioritize traffic and enhance network performance. Moreover, VLANs provide an extra layer of security by separating different groups of users or devices. For instance, a guest network can be created with restricted access privileges. This segregation not only improves security but also helps optimize network resources.
When considering the adoption of either subnets or VLANs, it is crucial to assess the network requirements thoroughly. If the primary goal is division at the IP level, subnets offer a reliable solution. If logical isolation at the data link level and enhanced network controls are necessary, VLANs are the way to go. Ultimately, making the right choice between subnets and VLANs ensures better access control, scalability, and overall network performance.
FAQ
What is VLAN?
VLAN stands for Virtual LAN, which is a network segmentation approach that divides a larger physical network into multiple smaller virtual networks. This segmentation enhances network security, efficiency, and flexibility.
What are the benefits of VLAN?
VLANs provide several benefits including isolation of broadcast domains, improved network security through the isolation of subnetworks, enhanced network management and scalability, and reduced scope of compliance by enabling auditing of specific subnets.
How does network segmentation differ from VLAN?
Network segmentation involves dividing a computer network into subnets or subnetworks, whereas VLANs create separate virtual networks within the same physical network. This division occurs at different levels (IP level for subnets, data link layer for VLANs), resulting in different configurations, terminologies, and functionalities.
When should I use subnets instead of VLANs?
Subnets are more suitable when there is a need to divide different networks at the IP level, create multiple IP addresses for each partition, and control access to specific sub-networks. Subnets are commonly used for internal and external network connectivity.
When should I use VLANs?
VLANs are suitable for creating isolated networks within the same physical network, prioritizing traffic within those networks, optimizing network performance, enhancing security, and establishing separate guest networks. The choice between subnets and VLANs depends on specific network requirements such as the need for IP-level division or logical isolation at the data link level.