Table of Contents
E-commerce, or electronic commerce, refers to the buying and selling of goods and services over an electronic network, primarily the internet. It involves the transmission of funds and data to facilitate online transactions. Modern shopping behaviors have been greatly impacted by the rise of e-commerce, reshaping the retail landscape in significant ways.
How Does E-commerce Work?
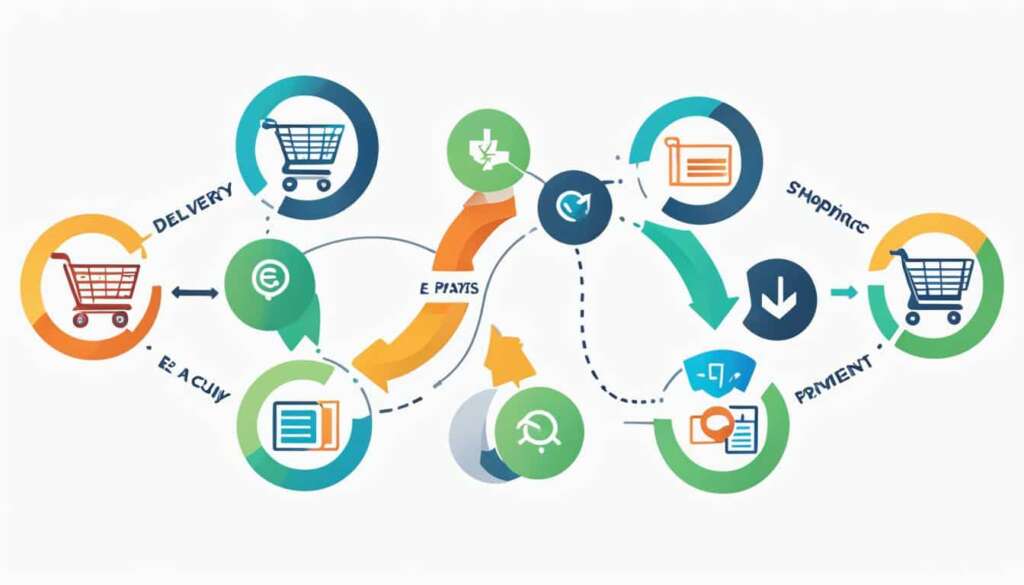
E-commerce transactions have revolutionized the way people shop, allowing them to conveniently access online stores through their own devices. With just a few clicks, customers can browse through a wide range of products and services, place orders, and make payments securely over the internet. But have you ever wondered what goes on behind the scenes to ensure a seamless shopping experience? Let’s dive into the inner workings of e-commerce to understand how it operates.
The Process of E-commerce Transactions
When a customer visits an online store, their web browser establishes a connection with the server hosting the e-commerce website. This connection allows them to view the product catalog, explore different categories, and read detailed descriptions. Once the customer finds the desired product and adds it to their cart, the order processing begins.
Data related to the order, such as the customer’s shipping address and payment details, is then relayed to an order manager. This order manager acts as the intermediary, connecting with databases for inventory management and payment processing. It ensures that the ordered product is available in the inventory and that the payment information is valid and secure.
Once the order is validated and all the necessary checks are complete, the customer is notified of the order status. This confirmation provides peace of mind, assuring the customer that their order has been received and is in progress. At this stage, the order data is sent to the warehouse or fulfillment department for product dispatch.
Inventory Management and Fulfilment
Efficient inventory management is crucial for successful e-commerce operations. Online stores rely on accurate and up-to-date inventory data to ensure that products listed on the website are available for purchase. Inventory management systems track stock levels, monitor product movement, and facilitate seamless replenishment when needed.
Once an order is received, the warehouse or fulfillment department receives the order data. They retrieve the product from the inventory, conduct quality checks, and prepare it for shipment. The ordered items are carefully packaged to ensure safe transportation and minimize the risk of damage. In some cases, e-commerce businesses may utilize third-party logistics services for efficient shipping and fulfillment.
Payment Processing in E-commerce
Secure payment processing is a critical component of e-commerce. Customers need assurance that their financial information is protected, especially when making online transactions. E-commerce platforms employ various payment gateways to enable secure transactions and protect sensitive data.
Payment gateways facilitate the secure transfer of funds between the customer and the online store. They encrypt payment information, verify the authenticity of the card or payment method, and ensure that the funds are transferred securely. Popular payment gateways include PayPal, Stripe, and Braintree, among others.
The Role of E-commerce Platforms
E-commerce platforms play a vital role in enabling smooth online transactions. They provide the necessary infrastructure and tools for businesses to set up and manage their online stores. These platforms can take the form of online marketplaces like Amazon and eBay, software as a service (SaaS) tools, or open source tools managed by companies.
Online marketplaces offer businesses a ready-made platform to showcase their products and reach a vast customer base. SaaS tools provide comprehensive e-commerce functionalities, including website creation, inventory management, and order processing. Open source tools, on the other hand, offer flexibility and customization options for businesses that require more control over their e-commerce operations.
To summarize, e-commerce transactions involve a seamless interaction between the customer’s web browser, the online store’s server, and various components such as order managers, inventory databases, payment gateways, and fulfillment departments. This seamless process ensures that customers can shop online efficiently, while businesses can manage their inventory, process payments, and fulfill orders seamlessly.
Types of E-commerce
In the world of e-commerce, there are various types of online transactions that cater to different needs and parties involved. Understanding these types can help businesses and consumers navigate the digital marketplace more effectively.
B2B E-commerce
B2B e-commerce, or business-to-business e-commerce, refers to transactions that occur between businesses. In this type of e-commerce, companies engage in buying and selling goods or services with one another. B2B e-commerce platforms facilitate interactions between suppliers, manufacturers, wholesalers, and retailers, streamlining the supply chain and promoting efficient business operations.
B2C E-commerce
B2C e-commerce, or business-to-consumer e-commerce, involves businesses selling products or services directly to consumers. This is the most common type of e-commerce that people encounter on a daily basis. B2C e-commerce platforms, such as online retail stores, allow businesses to reach a broader customer base and provide convenience for consumers to shop from the comfort of their homes.
D2C E-commerce
D2C e-commerce, or direct-to-consumer e-commerce, empowers businesses to sell their products or services directly to consumers without the need for intermediaries. This type of e-commerce allows companies to have more control over their brand image and customer experience. D2C e-commerce platforms enable businesses to build direct relationships with their customers, resulting in increased brand loyalty and customer engagement.
C2C E-commerce
C2C e-commerce, or consumer-to-consumer e-commerce, enables individual consumers to trade products and services with each other online. Online marketplaces, such as eBay and Craigslist, provide platforms for consumers to buy and sell pre-owned or handmade items. C2C e-commerce encourages peer-to-peer transactions and fosters a sense of community among consumers.
C2B E-commerce
C2B e-commerce, or consumer-to-business e-commerce, involves consumers offering their products or services to businesses. This type of e-commerce is commonly seen in the gig economy, where individuals provide freelance services or sell unique products to companies. C2B e-commerce platforms provide a marketplace for businesses to connect with talented individuals and acquire specialized services or products.
B2A E-commerce
B2A e-commerce, or business-to-administration e-commerce, focuses on transactions between businesses and government or public administration. It involves the exchange of goods, services, or information between companies and government entities. B2A e-commerce platforms streamline processes such as tax filing, license applications, and procurement for businesses interacting with government agencies.
C2A E-commerce
C2A e-commerce, or consumer-to-administration e-commerce, facilitates transactions between consumers and government or public administration. Citizens can use C2A e-commerce platforms to access government services, pay taxes, apply for permits, or submit official documents online. This type of e-commerce simplifies administrative processes, reduces paperwork, and enhances citizen-government interactions.
M-commerce
M-commerce, or mobile commerce, refers to online sales transactions conducted through mobile devices. With the increasing popularity of smartphones and tablets, m-commerce has become an essential part of the e-commerce landscape. Mobile apps and mobile-optimized websites allow consumers to shop on-the-go and provide businesses with an additional channel to reach their target audience.

Advantages of E-commerce
E-commerce brings numerous benefits to businesses and consumers alike. It has revolutionized the way we shop and conduct transactions, providing a convenient and efficient online marketplace for a wide range of products and services. Let’s explore the advantages of e-commerce in more detail:
1. Availability and Accessibility
E-commerce offers customers the freedom to shop whenever they want, 24/7. Unlike traditional brick-and-mortar stores with fixed opening hours, e-commerce platforms are always accessible. This round-the-clock availability ensures that customers can browse and make purchases at their convenience, without any time constraints or limitations.
2. Speed of Access and Wide Selection
With e-commerce, customers can quickly access a vast array of products and services at their fingertips. Online stores have the ability to showcase a much wider selection than physical stores, as there are no space constraints. This allows customers to browse and choose from a diverse range of options, ensuring they can find precisely what they’re looking for.
3. International Reach
E-commerce transcends geographical boundaries, enabling businesses to reach customers worldwide. This international reach eliminates the limitations of physical distance, opening up new markets and opportunities for businesses. It allows customers from different countries to access products and services that may not be available locally, expanding their choices and facilitating global trade.
4. Lower Cost
E-commerce offers significant cost advantages compared to traditional physical stores. With e-commerce, businesses can operate with lower overhead costs, as there is no need for expensive retail spaces, extensive inventory, or a large number of staff. These cost savings can be passed on to customers, resulting in competitive prices and potential discounts.
5. Personalization
E-commerce leverages customer data to personalize the shopping experience. By analyzing customer behavior, preferences, and purchase history, businesses can provide targeted product recommendations and tailored marketing campaigns. This personalization enhances customer satisfaction, helps to build long-term relationships, and increases the likelihood of repeat purchases.
6. Ease of Purchasing
E-commerce simplifies the purchasing process through digital payment options. Customers can make payments conveniently and securely, without the need for physical cash or lengthy transactions. Digital wallets, credit/debit cards, and mobile payment systems offer ease and speed, ensuring a smooth and seamless checkout experience.
“E-commerce offers customers the convenience of around-the-clock shopping, a wide selection of products, and the ability to reach global markets.” – [Business Name]
E-commerce truly offers a transformative shopping experience, with its many advantages catering to the evolving needs and preferences of modern consumers. The next section will explore the potential disadvantages of e-commerce and how businesses and consumers can address them.
Disadvantages of E-commerce
Despite its advantages, e-commerce also comes with a set of disadvantages that consumers should be aware of. These drawbacks include limited customer service, lack of product experience, wait time for product delivery, and security issues.
Limited Customer Service
One of the key disadvantages of e-commerce compared to physical stores is the limited customer service available. Unlike in-store shopping, where customers can interact with sales associates and receive assistance in real-time, e-commerce platforms often have fewer avenues for direct customer support. This can lead to frustration and hinder the overall shopping experience.
Lack of Product Experience
E-commerce can also present challenges in terms of experiencing products before making a purchase. In physical stores, customers have the opportunity to touch, feel, and try out products, allowing them to make more informed decisions. In contrast, online shopping relies on product descriptions, images, and reviews, which may not offer the same level of insight and engagement.
Wait Time for Product Delivery
Another disadvantage of e-commerce is the wait time for product shipping. While online retailers strive to provide prompt delivery, it can still take time for products to reach customers’ doorsteps. This delay can be frustrating, particularly for customers who are accustomed to immediate gratification from in-store purchases.
Security Issues
Security is a significant concern in e-commerce. Online transactions involve the sharing of sensitive personal and financial information, making customers vulnerable to potential fraud and data breaches. E-commerce platforms must prioritize robust security measures to protect customer data and build trust in online shopping.

E-commerce offers numerous benefits, but it’s important to consider these disadvantages and take necessary precautions to mitigate their impact. By understanding the limitations of e-commerce, consumers can make informed decisions and ensure a safe and satisfactory online shopping experience.
History of E-commerce
E-commerce has a rich history that originated in the 1960s with the advent of Electronic Data Interchange (EDI). This technology, which enabled the transfer of business documents between computers, laid the foundation for modern e-commerce. It allowed companies to exchange electronic invoices, purchase orders, and other essential documents, streamlining business transactions and reducing paperwork.
However, it wasn’t until 1994 that the first online transaction took place, marking a significant milestone in the evolution of e-commerce. This transaction occurred when a CD of Sting’s album “Ten Summoner’s Tales” was sold on the NetMarket platform, utilizing a secure online payment method. This groundbreaking event set the stage for the e-commerce revolution that would follow.
Since then, e-commerce has experienced exponential growth and continuous evolution, reshaping the retail landscape. Traditional brick-and-mortar retailers have had to adapt quickly to compete with the rise of online marketplaces such as Amazon, Alibaba, eBay, and Etsy.
These online marketplaces have revolutionized the way consumers shop, offering a vast array of products and services that were previously only available through traditional retailers. With a few clicks, shoppers can now access a global marketplace and have products delivered directly to their doorstep.
In addition, the introduction of new technologies and the increasing popularity of mobile devices have further fueled the growth of e-commerce. Consumers now have the convenience of shopping from anywhere, at any time, using their smartphones or tablets.
The Evolution of E-commerce:
| E-commerce Stage | Main Features |
|---|---|
| Emerging Stage | Introduction of Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) enabling document transfer between businesses. |
| First Online Transaction | The sale of Sting’s album “Ten Summoner’s Tales” on the NetMarket platform, establishing secure online payment methods. |
| Rise of Online Marketplaces | Amazon, Alibaba, eBay, and Etsy become prominent online marketplaces, offering a wide range of products and services. |
| New Technologies | Mobility and accessibility through smartphones and tablets drive further e-commerce growth. |
As e-commerce continues to evolve, traditional retailers and online marketplaces will need to adapt and find innovative ways to attract and retain customers in today’s digital age. The history of e-commerce and its ongoing evolution highlight the transformative power of technology in reshaping the way we shop and connect in the modern world.
Conclusion
E-commerce has revolutionized shopping and business practices, offering unparalleled convenience, an extensive range of products, and global accessibility. Despite its advantages and disadvantages, e-commerce continues to thrive, reshaping the retail landscape. As technology advances and consumer demand increases, the future of e-commerce looks promising. With businesses and consumers increasingly embracing online transactions, e-commerce is poised to play an even more significant role in the global economy.
The convenience provided by e-commerce allows customers to shop anytime, anywhere, eliminating the limitations of physical store hours. Additionally, the wide selection of products available through online platforms provides customers with countless choices at their fingertips. The global reach of e-commerce allows businesses to expand their markets beyond geographical boundaries, presenting new opportunities for growth and expansion.
As technology evolves, e-commerce is set to become even more seamless and personalized, catering to the unique preferences of each consumer. Advancements in artificial intelligence, data analytics, and mobile technologies will further enhance the customer experience, making online shopping even more effortless and intuitive.
As we move forward, e-commerce will continue to transform the way we shop and conduct business, bringing about a new era of digital commerce. Businesses that adapt and embrace the e-commerce revolution will position themselves for success in the ever-evolving market. The future of e-commerce is bright, promising exciting innovations and endless possibilities for businesses and consumers alike.
FAQ
What is e-commerce?
E-commerce, or electronic commerce, refers to the buying and selling of goods and services over the internet.
How does e-commerce work?
E-commerce works by enabling customers to access online stores through their devices, browse products, place orders, and make payments online.
What are the types of e-commerce?
E-commerce can be classified into several types, including B2B, B2C, D2C, C2C, C2B, B2A, C2A, and m-commerce.
What are the advantages of e-commerce?
E-commerce offers advantages such as around-the-clock availability, wide product selection, global reach, and lower operating costs.
What are the disadvantages of e-commerce?
E-commerce has some disadvantages, including limited customer service, inability to touch products before purchase, wait time for shipping, and security issues.
What is the history of e-commerce?
E-commerce has a history dating back to the 1960s with the use of Electronic Data Interchange. It has since evolved and disrupted the retail landscape.
What is the future of e-commerce?
With advancements in technology and increasing consumer demand, the future of e-commerce looks promising as it continues to reshape the retail landscape.