Table of Contents
The Bitcoin mining landscape has undergone significant changes since its inception. Today, miners are dealing with a complex and competitive industry that requires substantial investment in specialized hardware and access to cheap electricity.
The crypto market has evolved, and the costs associated with mining have increased. For large-scale mining companies, the costs can be as high as $82,000 to mine a single Bitcoin, which is currently valued at around $95,000.
To determine whether mining remains a viable investment, it’s essential to analyze the current costs, potential returns, and alternative approaches. Understanding the economics of Bitcoin mining is crucial before committing resources to this competitive industry.
The Current State of Bitcoin Mining
The state of Bitcoin mining in 2025 reflects a mix of growing network difficulty and adapting mining operations. As the Bitcoin network continues to evolve, miners face new challenges and opportunities.
Bitcoin Mining in 2025: Key Statistics
In April 2024, the fourth Bitcoin halving reduced the block reward to 3.125 BTC, significantly impacting miners’ revenue streams. Despite this, Bitcoin mining remains profitable in 2025 for operations with access to efficient hardware and low-cost electricity. The daily global revenue for Bitcoin mining was around $63 million USD per day in March 2024.
Recent Changes in Mining Profitability
Recent changes in mining profitability have been influenced by Bitcoin’s price volatility, rising electricity costs, and the growing sophistication of mining equipment. The increased network difficulty has also played a crucial role in shaping the mining landscape.
The Impact of the Latest Halving
The latest halving event in April 2024 had a profound impact on the Bitcoin mining industry. The reduction in block reward forced many smaller operations to reassess their business models, leading to a shift towards more efficient and cost-effective mining operations.
As stated by a leading cryptocurrency analyst,
“The halving event has accelerated the consolidation of mining operations, favoring larger, more efficient miners.”
The current state of Bitcoin mining is characterized by increased network difficulty, reduced block rewards, and a growing emphasis on efficient mining operations. As the industry continues to evolve, miners must adapt to these changes to remain profitable.
How Bitcoin Mining Actually Works
At its core, Bitcoin mining is about validating transactions and adding them to the blockchain, a process that requires powerful computers. Miners compete to solve complex mathematical problems, which helps secure the network and verify transactions.

The Technical Process Explained
The technical process of Bitcoin mining involves several key steps. Miners collect pending transactions, hash them into a block, and then repeatedly change a small piece of data (nonce) until they find a valid solution that meets the network’s difficulty target. This process requires significant computational power, measured in hashrate.
Block Rewards and Transaction Fees
Miners are incentivized to participate in the mining process through block rewards and transaction fees. Currently, the block reward stands at 3.125 BTC per block, and this number is programmed to halve approximately every four years. The next halving is scheduled for 2028, after which the reward will reduce to 1.5625 BTC.
“The reward (plus transaction fees) are paid to the miner who solved the puzzle first.”
Network Difficulty and Hashrate
The network difficulty automatically adjusts every 2016 blocks (roughly two weeks) to maintain a consistent 10-minute average block time, regardless of how much total hashrate is contributing to the network. As more miners join the network, the difficulty increases, requiring even more computational power to solve the mathematical problems.
As stated by a prominent cryptocurrency expert, “The hashrate is a measure of a miner’s computational power, and the more computing power a machine has, the more solutions (and hence, block rewards) a miner is likely to find.“
The Real Costs of Mining Bitcoin
The economics of Bitcoin mining involve significant expenses that must be carefully considered. While the potential rewards of mining Bitcoin can be substantial, the costs associated with this activity can be equally significant.
Mining Hardware Investment
The initial investment in mining hardware represents one of the most significant upfront costs. Modern ASIC miners, which are specialized computers designed solely for the purpose of mining Bitcoins, can range from $2,000 to $20,000 depending on their efficiency and computing power.
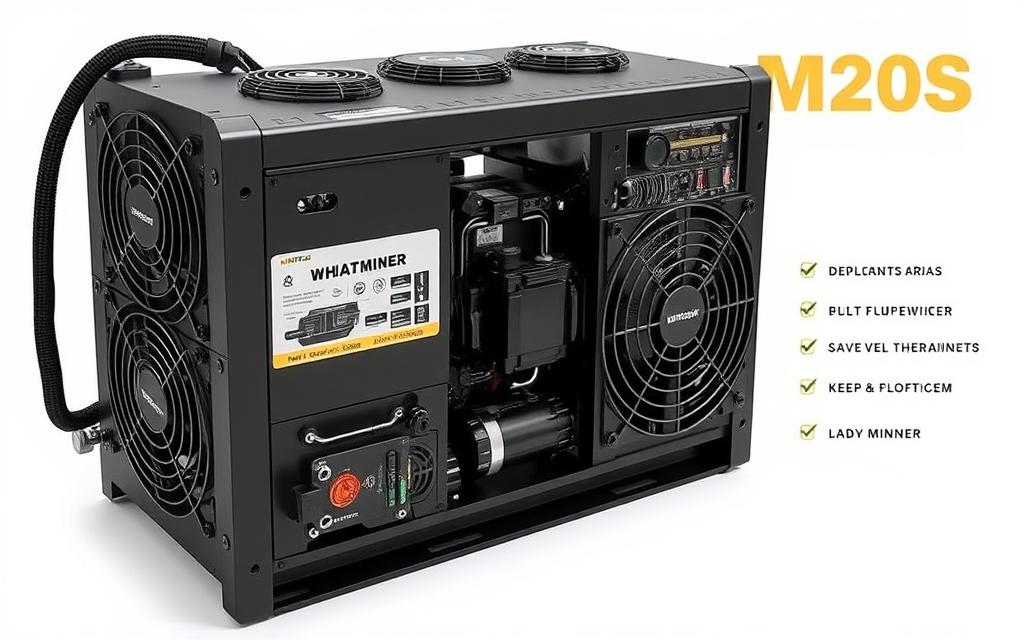

For instance, a Whatsminer M20S, a popular ASIC mining machine, can generate around $12 in Bitcoin revenue daily, depending on the current price of Bitcoin. However, the initial purchase price of such a machine is a significant outlay.
Electricity Consumption and Expenses
Electricity consumption is the primary ongoing expense for Bitcoin miners. The energy required to power these machines is substantial, and the cost of electricity can vary significantly depending on the location.
Professional mining operations seek locations with electricity rates below $0.05 per kWh to maintain profitability. At typical residential electricity rates in the United States ($0.12-$0.15 per kWh), most home miners operate at a loss unless they have access to subsidized power or alternative energy sources.
Additional Operational Costs
Beyond the initial hardware investment and ongoing electricity costs, there are additional operational costs to consider. These include cooling systems to mitigate the substantial heat generated by mining machines, maintenance, facility rental, internet connectivity, and security measures.
The energy efficiency of mining hardware is measured in watts per terahash (W/TH), with newer models offering better performance but at premium prices. Understanding these costs is crucial for determining the overall viability of a mining operation.
Potential Benefits and Rewards
The rewards of Bitcoin mining extend beyond mere financial gains. For many miners, the direct Bitcoin earnings from mining provide a steady stream of newly minted cryptocurrency without having to purchase it on exchanges, potentially offering better acquisition costs during bull markets.
Direct Bitcoin Earnings
Mining can be viewed as a dollar-cost averaging strategy where operational costs are exchanged for Bitcoin at production rates rather than market rates. This approach can help miners accumulate BTC over time, potentially at a lower average cost.
For instance, if BTC is priced at $9,000, a miner with an M20S machine can earn a daily revenue of $6.16. This steady income can be a significant incentive for miners, especially if they can manage their operational costs effectively.
Long-term Investment Perspective
From a long-term investment perspective, miners who can hold their earned Bitcoin through market cycles may benefit significantly from future price appreciation. Successfully mining just one Bitcoin block and holding onto it since 2010 would mean having around $5 million worth of Bitcoin in your wallet by 2025.
Professional mining operations often develop strategies to hedge against market volatility, including selling a portion of mined coins to cover operational expenses while holding the remainder. This strategy can help miners navigate the unpredictable nature of the cryptocurrency market.
Supporting the Bitcoin Network
Beyond financial rewards, miners contribute to the security and decentralization of the Bitcoin network, supporting the broader cryptocurrency ecosystem and potentially benefiting from network effects as adoption increases.
As mining profitability is closely tied to the overall health of the Bitcoin network, miners play a crucial role in maintaining the integrity of the blockchain. Their efforts help to secure transactions and ensure the continued operation of the network.
Is Mining Bitcoin Worth It for Different Miners?
As the Bitcoin mining landscape evolves, the question of whether mining is worth it depends on the type of miner. The profitability of mining Bitcoin varies significantly between individual miners and large-scale operations.
Home Miners vs. Professional Operations
Home miners face significantly different economics than professional mining operations. With higher electricity costs, limited access to the latest hardware, and challenges in managing heat and noise, home mining has become increasingly challenging. In contrast, professional mining operations benefit from economies of scale, including bulk hardware purchases, preferential electricity rates, and optimized facilities designed specifically for mining.
For instance, a home miner in the United States might pay up to $0.15 per kWh for electricity, while a large mining farm in Russia or Iceland might secure rates as low as $0.03 per kWh. This disparity significantly impacts the profitability of mining operations.
Geographic Considerations
Geographic considerations play a crucial role in mining profitability. Regions with low electricity costs (under $0.05/kWh) provide significant advantages to miners. Countries with cool climates also offer natural cooling advantages, reducing operational costs associated with preventing ASIC miners from overheating.
| Region | Average Electricity Cost ($/kWh) | Cooling Advantages |
|---|---|---|
| USA | 0.12 | Moderate |
| Russia | 0.03 | High |
| Iceland | 0.05 | High |
Scale Economics in Mining
The scale economics in mining create a widening gap between home miners and industrial operations. Large-scale mining operations can negotiate better terms with suppliers, power companies, and even cryptocurrency exchanges for selling mined coins. This makes it increasingly difficult for small miners to remain profitable as the difficulty of mining Bitcoin increases and the price lags behind.
In conclusion, while home miners face significant challenges, professional mining operations continue to thrive due to their scale and strategic location choices. As the mining landscape evolves, the gap between these two types of miners is likely to continue growing.
Mining Pools: A Necessary Strategy
In the current Bitcoin mining landscape, joining a mining pool has become a necessity for miners.
Mining pools have become essential for all Bitcoin miners as they combine the hashrate of multiple participants to increase the probability of finding blocks and provide a steady income. Without pool mining, a typical ASIC miner might wait years before successfully mining a block, making solo mining impractical for all but the largest operations.
How Mining Pools Work
Mining pools operate by aggregating the computing power of multiple miners to solve complex mathematical equations and validate transactions on the Bitcoin network. By working together, miners can increase their chances of finding a block and earning the associated block reward and transaction fees.
The most popular payout model used by mining pools is PPS+ (Pay Per Share Plus), which provides guaranteed payments to miners based on their contributed hashrate, regardless of whether the pool successfully mines a block.
Popular Mining Pools in 2025
Some of the most popular Bitcoin mining pools in 2025 include F2Pool, which supports around 15% of the entire Bitcoin network. F2Pool’s payout method is PPS+, taking the risk away from miners by paying out block rewards and transaction fees regardless of the pool’s luck in finding blocks.
Pool Fees and Payout Methods
Pool fees typically range from 1% to 3% of mining rewards, representing a worthwhile trade-off for the consistency and reduced variance in earnings that mining pools provide. When selecting a mining pool, miners should consider factors beyond fees, including reliability, transparency, geographic server distribution, and additional features like merged mining options.
By understanding how mining pools work and choosing the right pool, miners can maximize their earnings and remain competitive in the ever-evolving Bitcoin mining landscape.
Alternatives to Direct Mining
Beyond direct mining, various other strategies can provide a foothold in the Bitcoin and broader cryptocurrency ecosystem. These alternatives cater to different investment preferences and risk tolerances.
Cloud Mining Services
Cloud mining services offer an entry point for those interested in mining without the need for significant hardware investment. However, it’s crucial to note that contracts often come with high fees, and profitability can be questionable compared to direct investment in Bitcoin.

Mining Stocks and ETFs
Mining stocks and ETFs provide exposure to the mining industry through traditional financial markets. This allows investors to benefit from mining company performance without needing technical expertise in cryptocurrency mining.
Simply Buying and Holding Bitcoin
For many individuals, simply buying and holding Bitcoin often provides better returns than engaging in mining activities, especially for those without access to cheap electricity or the ability to operate at scale. This approach eliminates the need to worry about the operational risks associated with mining.
For those interested in exploring other cryptocurrencies to mine, visiting PC Site’s guide on new cryptocurrencies to mine for could be beneficial.
Conclusion: Making Your Mining Decision
Evaluating whether to engage in Bitcoin mining involves understanding both the potential rewards and the significant costs involved. The profitability of mining depends on a delicate balance of factors including electricity costs, hardware efficiency, the current Bitcoin price, network difficulty, and the scale of operations.
For home miners, the challenge is particularly daunting in regions with standard electricity rates. However, individuals with access to subsidized power or renewable energy sources may find viable opportunities. It’s crucial to conduct a thorough cost-benefit analysis, considering all expenses, potential returns, and the opportunity cost compared to directly purchasing Bitcoin.
Despite the challenges, mining still plays a vital role in the Bitcoin ecosystem. Those passionate about supporting the network may choose to mine even with slim margins. Looking ahead, advancements in mining hardware efficiency and the integration of renewable energy could make mining more accessible to smaller participants, potentially increasing network decentralization.
The future of Bitcoin mining may see improved profitability as ASIC mining hardware innovation reaches its limits and sustainable power solutions become more accessible. This could enable small individual miners to re-enter the network, further aligning with the original intentions of Satoshi Nakamoto.
FAQ
What are the key factors that affect the profitability of Bitcoin mining?
The profitability of Bitcoin mining is influenced by several factors, including the cost of electricity, the efficiency of mining hardware, the current block reward, and the overall network difficulty. Additionally, the price of BTC and the fees associated with mining pools also play a crucial role.
How does the block reward halving impact mining profitability?
The block reward halving reduces the number of new BTC awarded to miners for validating transactions, which can lead to decreased mining profitability unless the price of BTC increases accordingly. This reduction in supply can potentially drive up the price, but it’s not a guarantee.
What is the role of mining pools in the Bitcoin mining process?
Mining pools allow individual miners to combine their computing power, increasing their chances of solving complex mathematical equations and earning BTC. By pooling resources, miners can reduce the variance in their income and receive more consistent payouts.
How do electricity costs affect the viability of home mining operations?
Electricity costs are a significant expense for miners, and high costs can render home mining operations unprofitable. Miners must carefully consider their energy expenses and explore ways to minimize them, such as using energy-efficient mining hardware or relocating to areas with lower electricity rates.
What are the advantages of using ASIC miners over GPU miners?
ASIC miners are designed specifically for Bitcoin mining and offer significantly higher hash rates and energy efficiency compared to GPU miners. While GPU miners can be used for other tasks, ASIC miners are optimized for BTC mining, making them a more effective choice for serious miners.
Can cloud mining services be a viable alternative to direct mining?
Cloud mining services allow users to rent mining hardware and infrastructure, potentially reducing the upfront costs and technical complexities associated with direct mining. However, users must carefully evaluate the terms and conditions of these services, as they can come with significant fees and risks.
How does the network difficulty impact mining profitability?
As the network difficulty increases, miners need more powerful hardware to solve the complex mathematical equations required to validate transactions. This can lead to higher costs and reduced mining profitability unless the price of BTC increases accordingly.
What are the benefits of scale economics in Bitcoin mining?
Larger mining operations can take advantage of scale economics by negotiating lower electricity rates, reducing hardware costs, and improving operational efficiency. This enables them to maintain a competitive edge and increase their mining profitability.









