Table of Contents
Serial-Attached SCSI (SAS) is a method used for accessing computer peripheral devices, such as external hard disk drives and magnetic tape drives. It is a protocol for point-to-point serial transmissions between storage devices and computers, with data transferred one bit at a time. SAS systems include targets (storage drives), initiators (devices sending requests), a service delivery subsystem (linking targets with initiators), and expanders (enabling port expansion).
SAS is widely used in businesses with significant storage requirements, offering advantages over parallel SCSI and SATA in terms of transfer speeds, cable length, cost, and device capacity. SAS drives are preferred for servers and enterprise applications, while SATA drives are commonly used in personal computers.
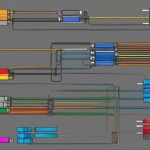
Check out the image below for a visual representation of a SAS drive:
Advantages and Disadvantages of SAS Drives
SAS drives offer several advantages over parallel SCSI and SATA drives.
- Thinner and longer cables: SAS drives use thinner and longer cables compared to parallel SCSI and SATA drives, allowing for easier cable management and increased flexibility in system design.
- Smaller connectors: SAS drives utilize smaller connectors, resulting in reduced space requirements and improved airflow within server enclosures.
- Higher transfer speeds: SAS drives support faster data transfer rates than parallel SCSI and SATA drives, enabling quicker access to stored information and improved overall system performance.
- Greater device capacity: SAS supports up to 65,535 devices on a single interface, while parallel SCSI only supports 16 devices. This scalability makes SAS drives ideal for large-scale storage environments.
- Better resistance to crosstalk: SAS technology incorporates advanced signal isolation techniques, minimizing crosstalk and ensuring data integrity even in densely populated storage configurations.
However, there are also some disadvantages associated with SAS drives:
- Parallel interfaces can be faster in certain cases: While SAS drives offer impressive transfer speeds, parallel interfaces may still outperform SAS in specific applications, particularly those reliant on legacy hardware.
- Cost: SAS drives are generally more expensive than SATA drives, making them less cost-effective for certain storage requirements.
- Optimized for specific use cases: SAS drives are designed for enterprise applications and are optimized for performance and reliability, whereas SATA drives are more commonly utilized for personal computing and storage purposes.
- Compatibility considerations: When utilizing SAS drives, it is essential to ensure compatibility with existing hardware and infrastructure, such as server backplanes and RAID controllers.
Despite these disadvantages, the advantages of SAS drives, including higher transfer speeds, enhanced data integrity, and support for larger-scale storage environments, make them a preferred choice for many business-critical applications.
For more information on SAS drives and their specific advantages and disadvantages, please refer to the table below:
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Thinner and longer cables | Parallel interfaces can be faster in certain cases |
| Smaller connectors | Cost |
| Higher transfer speeds | Optimized for specific use cases |
| Greater device capacity | Compatibility considerations |
| Better resistance to crosstalk |
SAS SSD vs. SATA SSD and PCIe
SAS SSDs (Serial-Attached SCSI solid-state drives) are NAND flash-based storage devices that utilize the SAS interface for high availability, high input/output, and low latency applications. These drives offer faster data transfer rates compared to SATA SSDs and come equipped with advanced features, including support for dual-port operation and enhanced reliability.
SAS SSDs are predominantly used in enterprise servers and storage arrays, where their high performance and robustness are crucial. The SAS interface enables SAS SSDs to handle heavy workloads and intensive data processing tasks with ease, making them the preferred choice for large-scale server applications.
On the other hand, SATA SSDs (Serial ATA solid-state drives) are also NAND flash-based storage devices but use the SATA interface. While SATA SSDs may not match the data transfer rates of SAS SSDs, they provide a more cost-effective solution for those focused on storage capacity.
Additionally, PCIe SSDs (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express solid-state drives) integrate flash storage directly onto the server motherboard. By eliminating the need to share a bus, PCIe SSDs offer exceptionally high data transfer rates, further enhancing performance.
When deciding between SAS SSDs, SATA SSDs, and PCIe SSDs, understanding the specific requirements of your application is crucial. If speed, reliability, and compatibility are the primary considerations, SAS SSDs are the optimal choice. However, if cost-effectiveness and storage capacity are the main priorities, SATA SSDs may be more suitable. It’s also essential to ensure compatibility with server backplanes when selecting either SAS or SATA drives.
| Feature | SAS SSD | SATA SSD | PCIe SSD |
|---|---|---|---|
| Data Transfer Rates | High | Moderate | Very High |
| Reliability | Excellent | Good | Excellent |
| Compatibility | Primarily used in enterprise servers and storage arrays | Commonly used in personal computers and consumer devices | Compatible with server motherboards |
Future of SAS SSDs and Considerations
The future of SAS SSDs looks promising with the upcoming SAS 4.0 specification. This new generation of SAS technology will bring increased speeds and enhanced data integrity to meet the demands of modern enterprise applications. SAS 4.0 will provide a full throughput per lane of 24 Gbps, allowing for faster and more efficient data transfers.
One of the key features of SAS 4.0 is forward error correction, which ensures the accuracy of transmitted data and reduces the risk of data corruption or loss. Additionally, SAS 4.0 will continuously adapt to optimize performance and maintain high levels of data integrity.
To fully leverage the benefits of SAS 4.0, compatible hardware components will be essential. RAID cards, expanders, and host bus adapters that support SAS 4.0 are expected to be available in 2018. It is crucial for businesses planning to adopt future SAS technologies to consider compatibility and hardware requirements for seamless integration.
SAS SSDs are known for their fast speeds, high reliability, and flexibility in terms of write endurance options. As the future of SAS SSDs unfolds with SAS 4.0, businesses can expect even greater performance and data integrity. However, it is important to stay informed about compatibility and plan for the hardware requirements necessary to embrace the advancements of SAS SSDs in the future.
FAQ
What is a SAS drive?
A SAS drive, also known as a Serial-Attached SCSI drive, is a method used for accessing computer peripheral devices such as external hard disk drives and magnetic tape drives. It is a protocol for point-to-point serial transmissions between storage devices and computers, with data transferred one bit at a time.
What are the advantages of SAS drives?
SAS drives offer several advantages over parallel SCSI and SATA drives. They have thinner and longer cables, smaller connectors, and higher transfer speeds. SAS supports up to 65,535 devices on an interface, while parallel SCSI only supports 16 devices. SAS also has better resistance to crosstalk and continues to be updated for expanded capabilities.
How do SAS drives compare to SATA drives?
When compared to SATA drives, SAS drives have higher throughput rates, better reliability, and support for longer cable runs. However, SATA drives are less expensive and more optimized for storage capacity. The choice between SAS and SATA depends on the specific requirements of the application.
What are SAS SSDs?
SAS SSDs, or Serial-Attached SCSI solid-state drives, are NAND flash-based storage devices that use the SAS interface for high availability, high input/output, and low latency applications. They provide faster data transfer rates compared to SATA SSDs and support dual-port operation and advanced features for reliability. SAS SSDs are primarily used in enterprise servers and storage arrays.
How do SAS SSDs compare to SATA SSDs and PCIe SSDs?
SAS SSDs are generally better suited for large server applications, while SATA SSDs are more cost-effective for capacity purposes. PCIe SSDs, on the other hand, integrate flash storage onto the server motherboard and offer high data transfer rates by eliminating the need to share a bus. It is important to ensure compatibility with server backplanes when choosing SAS or SATA drives.
What is the future of SAS SSDs?
The future of SAS SSDs includes the upcoming SAS 4.0 specification, which will increase the full throughput per lane to 24 Gbps. This next-generation SAS will also feature forward error correction and continuous adaptation to enhance data integrity and performance. RAID cards, expanders, and host bus adapters supporting SAS 4.0 are expected to be available in 2018. It is important to consider compatibility and hardware requirements when planning for future SAS technologies.