Table of Contents
Augmented reality (AR) is a cutting-edge technology with limitless potential in various industries. By integrating digital information with the user’s real-time environment, AR enhances their perception and interaction with the world around them.
Unlike virtual reality (VR), which immerses users in a completely artificial environment, AR blends digital and 3D components with the real world. This seamless integration can be experienced through smartphones, tablets, glasses, and other camera-equipped devices.
AR has a multitude of applications, ranging from decision-making aids to entertainment platforms. Its future potential is vast, with the power to revolutionize industries such as retail, entertainment, gaming, navigation, architecture, military, and archaeology.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve deeper into the world of augmented reality, exploring its functionalities, working principles, and examples of its real-world applications. Whether you are a technology enthusiast or a business professional, this guide will provide valuable insights into the immersive world of AR.
What is Augmented Reality (AR)?
Augmented reality (AR) is the integration of digital information with the user’s environment in real-time. It overlays digital elements onto the real world, allowing users to experience and interact with a modified version of their surroundings. Unlike virtual reality (VR), which transports users to a completely virtual environment, AR users remain in the real world while receiving additional digital information. AR can visually change natural environments or provide additional information to users. This technology blends digital and 3D components with the real world, enhancing the user’s perception and interaction.
AR technology uses devices such as smartphones, tablets, glasses, and headsets to overlay digital information onto the real-world environment. The user’s device captures the real-world environment and integrates computer-generated content seamlessly into the user’s view. This allows users to see and interact with digital elements in their physical surroundings.
In AR, the digital information can take various forms, including text, images, videos, 3D models, and interactive elements. These elements can be superimposed onto objects, surfaces, or locations in the real world, providing users with contextual information or enhancing their understanding of the environment.
AR has numerous applications across different fields and industries. It is used in education to create interactive learning experiences, in healthcare for medical training and visualization, in architecture and engineering for design and construction, and in tourism for virtual guided tours. It also has applications in entertainment, gaming, marketing, retail, and more.
AR has the potential to transform how we perceive and interact with the world around us. By overlaying digital information onto the real world, AR enhances our understanding, provides valuable insights, and creates immersive experiences that bridge the gap between the physical and digital realms.
Benefits of Augmented Reality
- Enhanced user experience by providing additional information and visual enhancements
- Improved decision-making by offering real-time data and contextual insights
- Increased efficiency and productivity through hands-free operation and interactive guidance
- Expanded learning opportunities with interactive and immersive educational experiences
- Better communication and collaboration through shared visualizations and annotations
- Increased customer engagement and brand loyalty through immersive marketing experiences
Challenges and Limitations of Augmented Reality
- Technological limitations such as hardware requirements and processing power
- Privacy and security concerns related to the collection and sharing of personal data
- Integration challenges when implementing AR in existing systems and workflows
- User acceptance and adoption hurdles due to unfamiliarity and perceived complexity
- Design considerations for creating intuitive and user-friendly AR experiences
Key Takeaways
Augmented reality (AR) is the integration of digital information with the real-world environment, enhancing the user’s perception and interaction. Unlike virtual reality, AR allows users to remain in their physical surroundings while receiving additional digital information. AR has various applications and benefits across industries, from education to entertainment. However, it also poses challenges, including technological limitations and user acceptance barriers.
How Does Augmented Reality Work?
Augmented reality (AR) technology utilizes a camera-equipped device, such as a smartphone or tablet, to capture the user’s real-world environment. By integrating computer vision, AR processes the camera’s input and identifies objects, enabling accurate tracking and mapping of the surroundings.
Once the environment is recognized and understood, computer-generated content is superimposed onto the real world, resulting in a seamless integration of digital information with the physical environment. This computer-generated content can include various elements like text, graphics, sounds, virtual objects, and even haptic feedback for tactile sensations.
Users can interact with these augmented elements, manipulating and experiencing them as if they were part of their immediate surroundings. This interactive and immersive experience of AR enhances the user’s perception and interaction with the environment, offering a truly transformative digital experience.
Enabling a Blended Reality
AR creates a blended reality by overlaying computer-generated content onto the user’s view of the real world. This seamless integration allows users to interact with digital information in context, enhancing their understanding and engagement.
AR brings a new dimension to our perception of reality, offering endless possibilities for entertainment, education, business, and more.
Applications of AR Technology
The applications of augmented reality are vast and diverse. From retail to entertainment, from navigation to architecture, and even in military and archaeology, AR has the potential to revolutionize numerous industries. Below are some key use cases of AR:
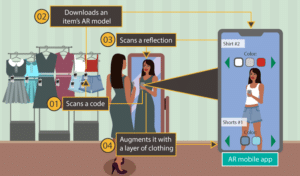
- Retail: AR can provide virtual try-ons, allowing customers to visualize how products will look before purchasing.
- Entertainment: AR gaming and interactive experiences like Snapchat filters enable users to engage with virtual elements in the real world.
- Navigation: AR can overlay routes and points of interest, enhancing the user’s navigation experience.
- Tools and Measurement: AR technology can facilitate measuring distances, angles, and other physical quantities.
- Architecture: AR visualization helps architects and designers showcase their ideas and present virtual models.
- Military: AR devices and systems assist soldiers in locating positions and accessing critical information in real-time.
- Archaeology: AR aids archaeologists in reconstructing ancient sites and visualizing historical contexts.
These examples represent just a fraction of the potential applications for AR, demonstrating the versatility and adaptability of this transformative technology.
Differences between AR and VR
When it comes to augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR), the main distinction lies in how they interact with reality. While both technologies offer immersive experiences, they do so in different ways.
Augmented reality (AR) enhances the user’s perception and interaction with the real-world environment by adding virtual information and elements. AR overlays digital content onto the user’s view of the real world, creating a blended experience. This technology keeps users grounded in their physical surroundings while providing additional visual layers of information or virtual objects.
Virtual reality (VR), on the other hand, completely replaces the real-world environment with a virtual one. VR immerses users in a digitally rendered environment that they can explore and interact with. By wearing specialized headsets or using VR devices, users are transported to a virtual environment that can be entirely different from their real-world surroundings.
AR and VR offer unique experiences that cater to different needs. AR enhances the real-world environment, while VR creates entirely new virtual environments for users to explore.
Key Differences between AR and VR:
- AR adds virtual information to the real-world environment.
- VR replaces the real-world environment with a virtual one.
- AR enhances the user’s perception and interaction with the real world.
- VR immerses users in a digitally rendered environment.
- AR overlays virtual data as a visual layer onto the real world.
- VR allows users to move around and interact with the virtual environment.

As the table and description above demonstrate, the core difference between AR and VR lies in their interaction with the real-world environment. While AR adds virtual elements to enhance the real world, VR completely replaces it with a virtual environment. Understanding this distinction is important when considering which technology to implement for different applications.
Top AR Use Cases
Augmented reality (AR) has a wide range of applications across various industries. Let’s explore some of the top use cases where AR is making a significant impact:
Retail
In the retail industry, AR is revolutionizing the way customers shop. By integrating AR into their online platforms, retailers can offer customers the ability to visualize products in their homes before making a purchase. For example, customers can use AR to see how furniture will look in their living rooms or try on virtual clothing to see how it fits.
Entertainment and Gaming
AR has transformed the entertainment and gaming industry by bringing virtual experiences into the real world. With AR, users can play games that overlay virtual elements onto their actual surroundings. For example, popular games like Pokemon Go allow players to catch virtual creatures in real-world locations using their smartphones.
Navigation
AR is also enhancing navigation experiences by providing users with real-time information and guidance. AR navigation apps can overlay routes onto the real world, making it easier for users to navigate unfamiliar areas. Additionally, AR can display information about local businesses, such as their operating hours or reviews, helping users make more informed decisions.
Tools and Measurement
In various industries, AR is being used as a powerful tool for measurement and visualization. For example, architects can use AR to create virtual models of buildings and visualize how they will fit into real-world environments. AR can also assist professionals in fields such as interior design, construction, and manufacturing by providing accurate measurements and visual representations of complex structures.
Military and Archaeology
The military and archaeological fields are leveraging the benefits of AR. In the military, AR provides soldiers with vital information, such as real-time data on the battlefield or instructions overlaid onto their line of sight. Archaeologists can use AR to digitally reconstruct ancient sites and visualize how they looked in their heyday, aiding in research and preservation efforts.
These are just a few examples of how AR is transforming various industries. As AR technology continues to advance, we can expect even more innovative applications that revolutionize the way we work, play, and interact with the world around us.
Examples of AR
Augmented Reality (AR) has gained popularity through various applications. The Target app, for instance, introduces the “See it in Your Space” feature, enabling customers to virtually place and view furniture in their homes. Through the Apple Measure app, smartphones can transform into virtual tape measures, allowing users to measure distances within their environment.
Snapchat filters utilize AR technology to overlay entertaining and interactive filters onto users’ snaps, adding an element of fun to their social media experience. Pokemon Go, a widely popular mobile AR game, uses GPS to detect virtual creatures in the real world, creating an immersive gaming experience for players.
Another notable example is Google Glass, a wearable AR device that provides users with hands-free access to information and applications. The U.S. Army employs Tactical Augmented Reality (TAR), an eyepiece equipped with AR technology, to assist soldiers in locating positions and accessing vital information during field operations.
These examples demonstrate the diverse range of applications for AR in various industries, from retail and entertainment to gaming and military applications. As AR technology continues to evolve, it is expected to revolutionize how we interact with the world around us.
FAQ
What is augmented reality (AR)?
Augmented reality is the integration of digital information with the user’s environment in real-time. It overlays digital features onto the real world, enhancing the user’s perception and interaction with their surroundings.
How does augmented reality work?
Augmented reality works by using a camera-equipped device, such as a smartphone or tablet, to capture the user’s real-world environment. The device’s camera identifies objects and uses computer vision to track and map the environment. Then, computer-generated content is overlayed onto the real world, creating a blended experience for the user.
What is the difference between augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR)?
The main difference between AR and VR lies in how they interact with reality. AR adds virtual information and elements to the real-world environment, enhancing the user’s perception and interaction. On the other hand, VR completely replaces the real-world environment with a virtual one, immersing the user in a digitally rendered environment.
What are the top use cases for augmented reality (AR)?
AR has a wide range of applications across various industries. It can be used in retail for visualizing products, entertainment and gaming for overlaying virtual games, navigation for displaying routes and information, tools and measurement for precise measurements, architecture visualization, military training, and archaeological research.
Can you provide examples of augmented reality (AR) applications?
Sure! Some popular examples include the Target app, which allows customers to virtually place and view furniture in their homes, the Apple Measure app that turns a smartphone into a virtual tape measure, Snapchat filters that overlay fun and interactive filters on user’s snaps, Pokemon Go which uses AR to detect virtual creatures in the real world, Google Glass that provides hands-free access to information, and the U.S. Army’s Tactical Augmented Reality (TAR) eyepiece for aiding soldiers in locating positions and accessing information in the field.