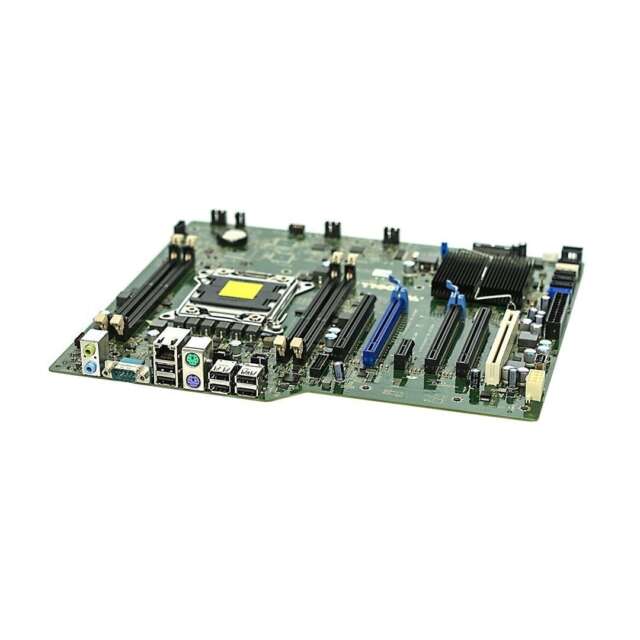
Table of Contents
Welcome to our in-depth exploration of the motherboard, the central nervous system of a computer. In this article, we will dive into the world of computer motherboards, understanding their role, exploring their various types, and uncovering the crucial components that make them tick. If you’re building or upgrading a computer system, understanding the ins and outs of motherboards is essential. So, let’s get started!
Components of a Motherboard
The motherboard consists of various components that enable its functionality. These include the CPU socket, memory slots, expansion slots, chipset, and connectors. Let’s take a closer look at each component:
CPU Socket
The CPU socket serves as the connection point for the CPU (Central Processing Unit), which is often referred to as the “brain” of the computer. The socket provides the necessary electrical connections and physical support for the CPU.
Memory Slots
Memory slots on the motherboard allow for the installation of RAM (Random Access Memory) modules. RAM is a crucial component that stores data and instructions for the CPU. The number and type of memory slots determine the maximum amount and speed of RAM that a computer can support.
Expansion Slots
Expansion slots are essential for adding peripherals and expansion cards to the motherboard. These slots, typically following the PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) standard, enable high-speed data transfer between the motherboard and expansion cards such as graphics cards, sound cards, and network cards. They provide users with the ability to customize their computer systems and accommodate future upgrades.
Chipset
The chipset is a crucial component on the motherboard that manages communication between different components. It acts as a bridge between the CPU, memory, storage devices, and other peripherals. The chipset determines the features and capabilities of a motherboard, such as the number of USB ports, SATA connectors, and support for technologies like overclocking.
Connectors
Connectors on the motherboard facilitate connectivity with external devices. These connectors include USB ports, audio jacks, Ethernet ports, and display connectors. They provide users with the ability to connect various devices and peripherals, such as keyboards, mice, monitors, and speakers, to their computers.
In summary, the components of a motherboard work together to ensure the proper functioning and connectivity of all computer parts. Understanding these components is essential for building or upgrading a computer system.
The Function of a Motherboard
When it comes to computer systems, the motherboard plays a vital role in ensuring seamless operation and optimal performance. This essential component serves three fundamental functions, each crucial to the overall functionality of the system.
Communication Hub
The motherboard acts as a central communication hub, facilitating the transfer of data between various components. It provides the necessary connections that allow the processor (CPU), memory, storage devices, and peripherals to communicate with each other. This seamless data transfer is essential for tasks such as running applications, accessing files, and operating peripherals.
Power Distribution
The motherboard serves as the power distribution center of the computer system. It receives power from the power supply unit (PSU) and distributes it to all the connected components. The motherboard ensures that each component receives the appropriate amount of power for operation. Without this crucial function, the computer would not be able to function.
System Control
In addition to communication and power distribution, the motherboard provides system control through firmware such as the Basic Input/Output System (BIOS) or Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI). This firmware initializes the hardware components during the startup process and allows users to configure various settings, such as boot order and hardware parameters.
Understanding these three functions of the motherboard is essential for anyone looking to optimize their computer system’s performance and operation. By acknowledging the motherboard’s role as a communication hub, power distributor, and system controller, users can make informed decisions and ensure the smooth functioning of their computer systems.
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Communication Hub | Facilitates data transfer between components |
| Power Distribution | Distributes power from the PSU to components |
| System Control | Initializes hardware and allows user configuration |
Types of RAM and Their Role in a Motherboard
RAM, or Random Access Memory, acts as the computer’s short-term memory and plays a crucial role within a motherboard. By understanding the different types of RAM available and their compatibility with motherboards, users can choose the right memory to optimize their computer system’s performance.
There are various types of RAM, each with its own performance implications. The most common types include DDR4 and DDR5. DDR4, which stands for Double Data Rate 4, is the previous generation RAM and has been widely used in recent years. DDR5, the latest generation, offers faster speeds and increased bandwidth, allowing for improved multitasking and overall system performance.
RAM allows for quick access to data that the CPU needs for processing, resulting in smoother multitasking and better application performance. The motherboard provides the necessary slots for installing RAM modules, ensuring compatibility and seamless integration.
It is important to note that not all motherboards support all types of RAM. Motherboards have specific RAM slots, and their compatibility depends on various factors such as the motherboard model, chipset, and the type of RAM used. Before purchasing RAM, it is crucial to check the motherboard’s specifications and ensure compatibility with the desired RAM type.
RAM Types Comparison
| RAM Type | Memory Speed | Bandwidth |
|---|---|---|
| DDR4 | 2133-3200 MHz | 17-25GB/s |
| DDR5 | 4800-8400 MHz | 40-70GB/s |
The table above provides a comparison of DDR4 and DDR5 RAM, showcasing the differences in memory speed and bandwidth. DDR5 offers significantly faster speeds and a higher bandwidth compared to DDR4, resulting in improved overall system performance.
When upgrading or building a computer system, understanding the role and compatibility of different RAM types within the motherboard is crucial. By choosing the right RAM, users can ensure optimal performance and enhance their computing experience.
Storage and Motherboards: HDDs vs. SSDs
When it comes to storage options for motherboards, two popular choices are hard disk drives (HDDs) and solid-state drives (SSDs). Each of these options has its own advantages and considerations, making it important to understand their differences to determine the best choice for your specific needs.
Hard Disk Drives (HDDs)
HDDs are known for offering larger storage capacity at a lower cost compared to SSDs. These drives consist of magnetic spinning disks that store and retrieve data. They have been a staple in computer storage for decades and are widely available in various capacities.
Solid-State Drives (SSDs)
On the other hand, SSDs provide faster read and write speeds and improved durability. Unlike HDDs, SSDs have no moving parts and use flash memory to store data. This technology allows for quicker data access and increased overall system performance.
SSDs are particularly beneficial in terms of their speed, which significantly reduces data loading times and enhances the overall responsiveness of a system. Additionally, their lack of moving parts makes them more resistant to shock and vibration, improving their durability compared to traditional HDDs.
It’s worth noting that SSDs are generally more expensive per unit of storage compared to HDDs. Therefore, if storage capacity is a top priority, HDDs might be the more cost-effective option. However, if speed, reliability, and system performance are crucial to your needs, an SSD may be the better choice.
Motherboard Storage Connectivity
The motherboard plays a significant role in providing the necessary connectors and interfaces for connecting both HDDs and SSDs. SATA (Serial ATA) connectors are commonly used for connecting storage drives to the motherboard. These connectors support both HDDs and SSDs, allowing for easy installation and integration into the system.
Overall, understanding the differences between HDDs and SSDs and considering your specific requirements will help you make an informed decision when it comes to choosing the right storage solution for your motherboard.
| Features | HDDs | SSDs |
|---|---|---|
| Storage Capacity | Higher capacity options available | Smaller capacity options, but continually increasing |
| Speed | Slower read/write speeds | Faster read/write speeds |
| Durability | Sensitive to shock and vibration due to moving parts | More durable, no moving parts |
| Cost | Lower cost per unit of storage | Higher cost per unit of storage |
| Power Consumption | Higher power consumption | Lower power consumption |
Expansion Slots and Customization Options
Motherboards come equipped with expansion slots that allow users to install additional components and expansion cards, providing ample customization options for their computer systems. These expansion slots, typically following the PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) standard, enable high-speed data transfer between the motherboard and expansion cards like graphics cards, sound cards, and network cards. By utilizing expansion slots, users can enhance their computer’s performance and tailor it to meet their specific needs.
Expansion slots offer a wide range of possibilities for customization. Users can install various expansion cards to add new features or upgrade existing ones. Whether it’s installing a high-performance graphics card for gaming or a dedicated sound card for superior audio quality, the expansion slots provide the flexibility to enhance and personalize the computer system.
Here are some common types of expansion cards that can be installed via the motherboard’s expansion slots:
- Graphics Cards: Graphics cards, also known as video cards or GPUs (Graphics Processing Units), are crucial for rendering high-quality graphics and videos. They are commonly used in gaming and multimedia applications.
- Sound Cards: Sound cards provide enhanced audio capabilities and superior sound quality, making them ideal for audio professionals, music enthusiasts, and gamers seeking immersive audio experiences.
- Network Cards: Network cards, also called NICs (Network Interface Cards), allow for faster and more stable internet connections, making them beneficial for online gamers and professionals who require reliable network connectivity.
- Storage Cards: Storage cards, such as RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) controllers, enable users to configure multiple storage devices for improved data protection, performance, and capacity.
- Modem Cards: Modem cards facilitate internet connectivity, particularly for users still relying on dial-up connections.
- USB and FireWire Cards: These expansion cards provide additional USB or FireWire ports, allowing users to connect more external devices to their computer system.
- Wi-Fi and Bluetooth Cards: Wi-Fi and Bluetooth expansion cards enable wireless connectivity, allowing users to connect to wireless networks and utilize Bluetooth-enabled devices.
With expansion slots available on motherboards, users can easily install these expansion cards and enjoy the benefits of expanded functionality and performance. Additionally, expansion slots also allow for future upgrades. As technology advances and new components become available, users can simply replace or add expansion cards to keep their systems up to date.
The image below demonstrates the various expansion slots commonly found on a motherboard:
| Expansion Slot | Description |
|---|---|
| The expansion slots on a motherboard provide connectivity options for expansion cards. |
Conclusion
The motherboard is an indispensable component of a computer system, acting as the central hub for communication, power distribution, and system control. It plays a crucial role in ensuring optimal performance and functionality in a computer system. By understanding the various components, functions, and types of motherboards, users can make informed decisions when building or upgrading their computer systems, ultimately enhancing their computing experience.
From the CPU socket to the expansion slots, each component on the motherboard contributes to the seamless operation of the entire system. The CPU socket provides a connection point for the processor, allowing for efficient data processing. The expansion slots enable the addition of peripherals and expansion cards, expanding the system’s capabilities and customization options. The memory slots facilitate the installation of RAM, optimizing multitasking and overall system performance.
Furthermore, the motherboard’s function extends beyond mere hardware connectivity. It also plays a role in power distribution, ensuring that each component receives the necessary power supply for operation. Additionally, the motherboard’s firmware, such as the BIOS or UEFI, enables system control and provides users with the ability to configure settings according to their preferences.
With a comprehensive understanding of motherboards, users can confidently choose the most suitable motherboard for their computer system, considering factors such as form factor, compatibility, and expansion capabilities. By delving into the intricacies of motherboards, users can unlock the true potential of their computer systems and achieve an optimized computing experience.
FAQ
What is a motherboard?
A motherboard is a crucial component in a computer system that serves as the central nervous system, connecting and facilitating communication between all other computer components.
What are the components of a motherboard?
The components of a motherboard include the CPU socket, memory slots, expansion slots, chipset, and connectors.
What is the function of a motherboard?
The motherboard serves as a communication hub, distributes power to components, and provides system control through firmware.
What are the different types of RAM and their role in a motherboard?
There are different types of RAM, such as DDR4 and DDR5, which serve as the computer’s short-term memory and ensure smooth multitasking and application performance.
What is the difference between HDDs and SSDs in terms of storage and motherboards?
HDDs offer larger storage capacity at a lower cost, while SSDs provide faster read and write speeds and improved durability.
What are expansion slots in a motherboard and how do they provide customization options?
Expansion slots allow for the installation of additional components and expansion cards, such as graphics cards, sound cards, and network cards, providing customization options and room for future upgrades.
How do I choose the right motherboard for my computer system?
When choosing a motherboard, consider factors such as form factor, compatibility with other components, and specific feature requirements.
Can I upgrade my motherboard?
Yes, you can upgrade your motherboard, but it may require replacing other components and ensuring compatibility with existing hardware.
What are the best motherboards on the market?
The best motherboards on the market vary depending on specific needs and preferences. It is recommended to research and consider factors such as performance, features, and budget.









